Long-Term Epigenetic Regulation of Foxo3 Expression in Neonatal Valproate-Exposed Rat Hippocampus with Sex-Related Differences
- PMID: 38791325
- PMCID: PMC11121443
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25105287
Long-Term Epigenetic Regulation of Foxo3 Expression in Neonatal Valproate-Exposed Rat Hippocampus with Sex-Related Differences
Abstract
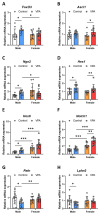
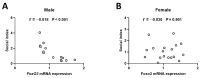
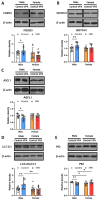
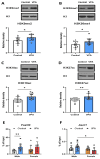
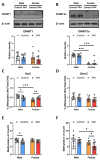
Perinatal exposure to valproic acid is commonly used for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) animal model development. The inhibition of histone deacetylases by VPA has been proposed to induce epigenetic changes during neurodevelopment, but the specific alterations in genetic expression underlying ASD-like behavioral changes remain unclear. We used qPCR-based gene expression and epigenetics tools and Western blotting in the hippocampi of neonatal valproic acid-exposed animals at 4 weeks of age and conducted the social interaction test to detect behavioral changes. Significant alterations in gene expression were observed in males, particularly concerning mRNA expression of Foxo3, which was significantly associated with behavioral changes. Moreover, notable differences were observed in H3K27ac chromatin immunoprecipitation, quantitative PCR (ChIP-qPCR), and methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme-based qPCR targeting the Foxo3 gene promoter region. These findings provide evidence that epigenetically regulated hippocampal Foxo3 expression may influence social interaction-related behavioral changes. Furthermore, identifying sex-specific gene expression and epigenetic changes in this model may elucidate the sex disparity observed in autism spectrum disorder prevalence.
Keywords: Ascl1; Foxo3; autism spectrum disorder; epigenetics; valproic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tordjman S., Somogyi E., Coulon N., Kermarrec S., Cohen D., Bronsard G., Bonnot O., Weismann-Arcache C., Botbol M., Lauth B., et al. Gene × Environment Interactions in Autism Spectrum Disorders: Role of Epigenetic Mechanisms. Front. Psychiatry. 2014;5:53. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

