Dopamine Pharmacodynamics: New Insights
- PMID: 38791331
- PMCID: PMC11121567
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25105293
Dopamine Pharmacodynamics: New Insights
Abstract
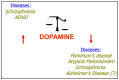
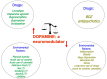
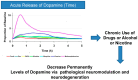
Dopamine is a key neurotransmitter involved in physiological processes such as motor control, motivation, reward, cognitive function, and maternal and reproductive behaviors. Therefore, dysfunctions of the dopaminergic system are related to a plethora of human diseases. Dopamine, via different circuitries implicated in compulsive behavior, reward, and habit formation, also represents a key player in substance use disorder and the formation and perpetuation of mechanisms leading to addiction. Here, we propose dopamine as a model not only of neurotransmission but also of neuromodulation capable of modifying neuronal architecture. Abuse of substances like methamphetamine, cocaine, and alcohol and their consumption over time can induce changes in neuronal activities. These modifications lead to synaptic plasticity and finally to morphological and functional changes, starting from maladaptive neuro-modulation and ending in neurodegeneration.
Keywords: addiction; dopamine; neuromodulation; neurotoxicity; reward system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lauretani F., Ruffini L., Testa C., Salvi M., Scarlattei M., Baldari G., Zucchini I., Lorenzi B., Cattabiani C., Maggio M. Cognitive and Behavior Deficits in Parkinson’s Disease with Alteration of FDG-PET Irrespective of Age. Geriatrics. 2021;6:110. doi: 10.3390/geriatrics6040110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

