AFB1 Toxicity in Human Food and Animal Feed Consumption: A Review of Experimental Treatments and Preventive Measures
- PMID: 38791343
- PMCID: PMC11121597
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25105305
AFB1 Toxicity in Human Food and Animal Feed Consumption: A Review of Experimental Treatments and Preventive Measures
Abstract
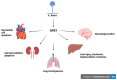
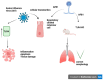
Aims: The current review aims to outline and summarize the latest research on aflatoxin, with research studies describing natural, herbal and chemical compound applications in animal (pig) models and in vitro cellular studies. Aflatoxin, a carcinogenic toxin metabolite, is produced by Aspergillus flavus in humid environments, posing a threat to human health and crop production. The current treatment involves the prevention of exposure to aflatoxin and counteracting its harmful toxic effects, enabling survival and research studies on an antidote for aflatoxin.
Objectives: To summarize current research prospects and to outline the influence of aflatoxin on animal forage in farm production, food and crop processing. The research application of remedies to treat aflatoxin is undergoing development to pinpoint biochemical pathways responsible for aflatoxin effects transmission and actions of treatment.
Significance: To underline the environmental stress of aflatoxin on meat and dairy products; to describe clinical syndromes associated with aflatoxicosis on human health that are counteracted with proposed treatment and preventive interventions. To understand how to improve the health of farm animals with feed conditions.
Keywords: Aspergillus flavus; aflatoxin; animal model; pig.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The impact of aflatoxin B1 on animal health: Metabolic processes, detection methods, and preventive measures.Toxicon. 2025 Feb;255:108262. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2025.108262. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Toxicon. 2025. PMID: 39855607 Review.
-
Exogenous β-aminobutyric acid application attenuates Aspergillus decay, minimizes aflatoxin B1 accumulation, and maintains nutritional quality in fresh-in-hull pistachio kernels.J Sci Food Agric. 2020 Mar 30;100(5):2130-2135. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10236. Epub 2020 Jan 14. J Sci Food Agric. 2020. PMID: 31884686
-
Reduction of aflatoxin B1 in chicken feed by using Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Rhizopus oligosporus and their combination.Mycopathologia. 2006 Oct;162(4):307-11. doi: 10.1007/s11046-006-0047-4. Mycopathologia. 2006. PMID: 17039279
-
Harmful Effects and Control Strategies of Aflatoxin B₁ Produced by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus Strains on Poultry: Review.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Mar 23;11(3):176. doi: 10.3390/toxins11030176. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30909549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ageratum conyzoides essential oil as aflatoxin suppressor of Aspergillus flavus.Int J Food Microbiol. 2010 Jan 31;137(1):55-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.10.017. Epub 2009 Oct 24. Int J Food Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19906457
Cited by
-
Bacillus CotA laccase improved the intestinal health, amino acid metabolism and hepatic metabolic capacity of Pekin ducks fed naturally contaminated AFB1 diet.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 10;15(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s40104-024-01091-8. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39385285 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Baicalin on Aflatoxin B1-Induced Growth Performance and Liver Health in Ducklings.Animals (Basel). 2025 Aug 8;15(16):2325. doi: 10.3390/ani15162325. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867655 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of AFB1, OTA, TCNs, and Patulin in Forensic Sciences: Applications in Autopsy, Criminal Investigations, and Public Health Prevention.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Nov 28;16(12):514. doi: 10.3390/toxins16120514. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39728772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Freitas C.H., Gonçalves C.L., da Silva Nascente P. Aflatoxins B1 and M1: Risks related to milk produced in Brazil. Ann. Microbiol. 2018;68:793–802. doi: 10.1007/s13213-018-1395-2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

