Potential Exosome Biomarkers for Parkinson's Disease Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38791346
- PMCID: PMC11121363
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25105307
Potential Exosome Biomarkers for Parkinson's Disease Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease worldwide. Given its prevalence, reliable biomarkers for early diagnosis are required. Exosomal proteins within extracellular nanovesicles are promising candidates for diagnostic, screening, prognostic, and disease monitoring purposes in neurological diseases such as PD. This review aims to evaluate the potential of extracellular vesicle proteins or miRNAs as biomarkers for PD. A comprehensive literature search until January 2024 was conducted across multiple databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library, to identify relevant studies reporting exosome biomarkers in blood samples from PD patients. Out of 417 articles screened, 47 studies were selected for analysis. Among exosomal protein biomarkers, α-synuclein, tau, Amyloid β 1-42, and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12) were identified as significant markers for PD. Concerning miRNA biomarkers, miRNA-24, miR-23b-3p, miR-195-3p, miR-29c, and mir-331-5p are promising across studies. α-synuclein exhibited increased levels in PD patients compared to control groups in twenty-one studies, while a decrease was observed in three studies. Our meta-analysis revealed a significant difference in total exosomal α-synuclein levels between PD patients and healthy controls (standardized mean difference [SMD] = 1.369, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.893 to 1.846, p < 0.001), although these results are limited by data availability. Furthermore, α-synuclein levels significantly differ between PD patients and healthy controls (SMD = 1.471, 95% CI = 0.941 to 2.002, p < 0.001). In conclusion, certain exosomal proteins and multiple miRNAs could serve as potential biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis prediction, and assessment of disease progression in PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; blood biomarker; exosome; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
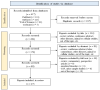
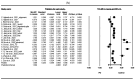

References
-
- Schapira A.H.V. Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Bailliere Clin. Neurol. 1997;6:15–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

