Comparison of Antimicrobial Properties of Graphene Oxide-Based Materials, Carbon Dots, and Their Combinations Deposited on Cotton Fabrics
- PMID: 38791366
- PMCID: PMC11121348
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25105328
Comparison of Antimicrobial Properties of Graphene Oxide-Based Materials, Carbon Dots, and Their Combinations Deposited on Cotton Fabrics
Abstract
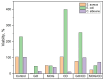
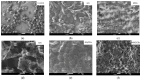
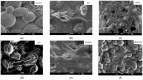
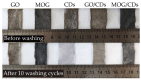
The rise in the antibiotic resistance of bacteria has increased scientific interest in the study of materials with unique mechanisms of antimicrobial action. This paper presents the results of studies on the antimicrobial activity of carbon materials and textiles decorated with them. A comparative analysis of the bactericidal and fungicidal activities of graphene oxide, electrochemically exfoliated multigraphene, carbon dots, and their combinations was performed. Microbiological studies on reference strains of E. coli, S. aureus, and C. albicans showed that graphene oxide inhibited growth with up to 98% efficiency. Electrochemically exfoliated multigraphene was less effective (up to 40%). This study found no significant antimicrobial activity of carbon dots and the combination of carbon dots with graphene oxide significantly weakened their effectiveness. However, the combination of electrochemically exfoliated multigraphene and carbon dots exhibits a synergistic effect (up to 76%). A study on the antimicrobial activity of decorated cotton textiles demonstrated the effectiveness of antimicrobial textiles with graphene oxide, electrochemically exfoliated multigraphene, and a combination of carbon dots with electrochemically exfoliated multigraphene.
Keywords: antimicrobial nanomaterials; antimicrobial textiles; carbon dots; electrochemically exfoliated multigraphene; graphene oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Graphene- and Nanoparticle-Embedded Antimicrobial and Biocompatible Cotton/Silk Fabrics for Protective Clothing.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021 Aug 16;4(8):6175-6185. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.1c00508. Epub 2021 Aug 5. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021. PMID: 35006896
-
Highly Washable and Conductive Cotton E-textiles Based on Electrochemically Exfoliated Graphene.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;16(3):958. doi: 10.3390/ma16030958. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36769966 Free PMC article.
-
A one-step process for the antimicrobial finishing of textiles with crystalline TiO2 nanoparticles.Chemistry. 2012 Apr 10;18(15):4575-82. doi: 10.1002/chem.201101683. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Chemistry. 2012. PMID: 22407609
-
Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-Based Functional Nanomaterials for Effective Antimicrobial Applications.Chem Rec. 2020 Dec;20(12):1505-1515. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202000090. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Chem Rec. 2020. PMID: 32975907 Review.
-
Recent Advances on Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Cotton Fabrics Containing Nanostructures.Molecules. 2021 May 18;26(10):3008. doi: 10.3390/molecules26103008. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34070166 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Carbon Dots as an Emergent Class of Sustainable Antifungal Agents.ACS Nano. 2025 Jul 15;19(27):24377-24403. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c03934. Epub 2025 Jul 2. ACS Nano. 2025. PMID: 40601415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural, Morphological, and Antibacterial Attributes of Graphene Oxide Prepared by Hummers' and Brodie's Methods.Molecules. 2025 Jan 9;30(2):240. doi: 10.3390/molecules30020240. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39860110 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Synthesis of Zinc Oxide on Cotton Fabric by Cathodic Cage Plasma Deposition for Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Performance.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 23;25(18):10192. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810192. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li P., Sun L., Xue S., Qu D., An L., Wang X., Sun Z. Recent advances of carbon dots as new antimicrobial agents. SmartMat. 2022;3:226–248. doi: 10.1002/smm2.1131. - DOI
-
- Gao W., editor. Graphene Oxide: Reduction Recipes, Spectroscopy, and Applications. 1st ed. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2015. The chemistry of graphene oxide; pp. 61–95.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

