Potential Role and Mechanism of Mulberry Extract in Immune Modulation: Focus on Chemical Compositions, Mechanistic Insights, and Extraction Techniques
- PMID: 38791372
- PMCID: PMC11121110
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25105333
Potential Role and Mechanism of Mulberry Extract in Immune Modulation: Focus on Chemical Compositions, Mechanistic Insights, and Extraction Techniques
Abstract
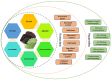
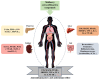
Mulberry is a rapidly growing plant that thrives in diverse climatic, topographical, and soil types, spanning temperature and temperate countries. Mulberry plants are valued as functional foods for their abundant chemical composition, serving as a significant reservoir of bioactive compounds like proteins, polysaccharides, phenolics, and flavonoids. Moreover, these compounds displayed potent antioxidant activity by scavenging free radicals, inhibiting reactive oxygen species generation, and restoring elevated nitric oxide production induced by LPS stimulation through the downregulation of inducible NO synthase expression. Active components like oxyresveratrol found in Morus demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting leukocyte migration through the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Gallic and chlorogenic acids in mulberry leaves (ML) powder-modulated TNF, IL-6, and IRS1 proteins, improving various inflammatory conditions by immune system modulation. As we delve deeper into understanding its anti-inflammatory potential and how it works therapeutically, it is crucial to refine the extraction process to enhance the effectiveness of its bioactive elements. Recent advancements in extraction techniques, such as solid-liquid extraction, pressurized liquid extraction, superficial fluid extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, and ultrasonic-assisted extraction, are being explored. Among the extraction methods tested, including Soxhlet extraction, maceration, and ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), UAE demonstrated superior efficiency in extracting bioactive compounds from mulberry leaves. Overall, this comprehensive review sheds light on the potential of mulberry as a natural immunomodulatory agent and provides insights into its mechanisms of action for future research and therapeutic applications.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; bioactive components; immune modulation; mulberry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity on LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells of White Mulberry (Morus alba L.) Leaf Extracts.Molecules. 2023 May 28;28(11):4395. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114395. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37298871 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of White Mulberry (Morus alba L.) Fruits on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages.Molecules. 2021 Feb 9;26(4):920. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040920. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33572374 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound extraction of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves and their effect on enhancing antioxidant activity.Carbohydr Polym. 2016 Feb 10;137:473-479. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.016. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Carbohydr Polym. 2016. PMID: 26686153
-
Extraction, purification, structural modification, activities and application of polysaccharides from different parts of mulberry.Food Funct. 2024 Apr 22;15(8):3939-3958. doi: 10.1039/d3fo05747j. Food Funct. 2024. PMID: 38536669 Review.
-
Mulberry leaves and their potential effects against cardiometabolic risks: a review of chemical compositions, biological properties and clinical efficacy.Pharm Biol. 2018 Dec;56(1):109-118. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1424210. Pharm Biol. 2018. PMID: 29347857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking Gut Health: The Potent Role of Stilbenoids in Intestinal Homeostasis.Animals (Basel). 2025 Feb 3;15(3):417. doi: 10.3390/ani15030417. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39943187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomics and microbiome insights reveal the protective mechanism of mulberry-derived postbiotics against inflammation in LPS-induced mice.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 18;16:1536694. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1536694. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40040706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saini P., Rohela G.K., Kumar J.S., Shabnam A.A., Kumar A. Cultivation, Utilization, and Economic Benefits of Mulberry. In: Gnanesh B.N., Vijayan K., editors. The Mulberry Genome. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2023. pp. 13–56.
-
- Yiğit D., Akar F., Baydaş E., Buyukyildiz M. Elemental Composition of Various Mulberry Species. Asian J. Chem. 2010;22:3554–3560.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

