Human and Murine Toll-like Receptor-Driven Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 38791389
- PMCID: PMC11120885
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25105351
Human and Murine Toll-like Receptor-Driven Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
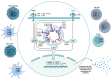
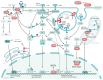
The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is linked to the differential roles of toll-like receptors (TLRs), particularly TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9. TLR7 overexpression or gene duplication, as seen with the Y-linked autoimmune accelerator (Yaa) locus or TLR7 agonist imiquimod, correlates with increased SLE severity, and specific TLR7 polymorphisms and gain-of-function variants are associated with enhanced SLE susceptibility and severity. In addition, the X-chromosome location of TLR7 and its escape from X-chromosome inactivation provide a genetic basis for female predominance in SLE. The absence of TLR8 and TLR9 have been shown to exacerbate the detrimental effects of TLR7, leading to upregulated TLR7 activity and increased disease severity in mouse models of SLE. The regulatory functions of TLR8 and TLR9 have been proposed to involve competition for the endosomal trafficking chaperone UNC93B1. However, recent evidence implies more direct, regulatory functions of TLR9 on TLR7 activity. The association between age-associated B cells (ABCs) and autoantibody production positions these cells as potential targets for treatment in SLE, but the lack of specific markers necessitates further research for precise therapeutic intervention. Therapeutically, targeting TLRs is a promising strategy for SLE treatment, with drugs like hydroxychloroquine already in clinical use.
Keywords: mouse models; systemic lupus erythematosus; toll-like receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
UNC93B1 variants underlie TLR7-dependent autoimmunity.Sci Immunol. 2024 Feb 23;9(92):eadi9769. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adi9769. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Sci Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38207055
-
Dosage of X-linked Toll-like receptor 8 determines gender differences in the development of systemic lupus erythematosus.Eur J Immunol. 2014 May;44(5):1503-16. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344283. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24500834 Free PMC article.
-
TLR8 on dendritic cells and TLR9 on B cells restrain TLR7-mediated spontaneous autoimmunity in C57BL/6 mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 28;111(4):1497-502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1314121111. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24474776 Free PMC article.
-
Female predisposition to TLR7-driven autoimmunity: gene dosage and the escape from X chromosome inactivation.Semin Immunopathol. 2019 Mar;41(2):153-164. doi: 10.1007/s00281-018-0712-y. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Semin Immunopathol. 2019. PMID: 30276444 Review.
-
Toll-like receptor signalling in B cells during systemic lupus erythematosus.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021 Feb;17(2):98-108. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00544-4. Epub 2020 Dec 18. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33339987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Mechanisms and Biomarkers in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 15;25(18):9965. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189965. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337453 Free PMC article.
-
The toll like receptor 7 pathway and the sex bias of systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 20;16:1479814. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1479814. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40051623 Free PMC article.
-
An exploration of the natural and acquired immunological mechanisms to high-risk human papillomavirus infection and unmasking immune escape in cervical cancer: A concise synopsis.Tzu Chi Med J. 2024 Dec 3;37(1):28-41. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_134_24. eCollection 2025 Jan-Mar. Tzu Chi Med J. 2024. PMID: 39850385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The story of clobenpropit and CXCR4: can be an effective drug in cancer and autoimmune diseases?Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 12;15:1410104. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1410104. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39070795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the role of APRIL in autoimmunity: implications for therapeutic targeting in systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjögren's syndrome.Front Immunol. 2025 Aug 1;16:1523392. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1523392. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40821822 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aringer M., Costenbader K., Daikh D., Brinks R., Mosca M., Ramsey-Goldman R., Smolen J.S., Wofsy D., Boumpas D.T., Kamen D.L., et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019;78:1151–1159. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214819. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

