Metabolite Profiling and Biological Activity Assessment of Paeonia ostii Anthers and Pollen Using UPLC-QTOF-MS
- PMID: 38791503
- PMCID: PMC11121493
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25105462
Metabolite Profiling and Biological Activity Assessment of Paeonia ostii Anthers and Pollen Using UPLC-QTOF-MS
Abstract
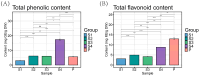
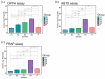
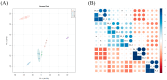
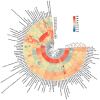
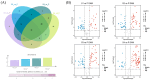
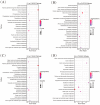
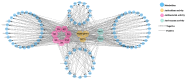
Paeonia ostii is an important economic oil and medicinal crop. Its anthers are often used to make tea in China with beneficial effects on human health. However, the metabolite profiles, as well as potential biological activities of P. ostii anthers and the pollen within anthers have not been systematically analyzed, which hinders the improvement of P. ostii utilization. With comprehensive untargeted metabolomic analysis using UPLC-QTOF-MS, we identified a total of 105 metabolites in anthers and pollen, mainly including phenylpropanoids, polyketides, organic acids, benzenoids, lipids, and organic oxygen compounds. Multivariate statistical analysis revealed the metabolite differences between anthers and pollen, with higher carbohydrates and flavonoids content in pollen and higher phenolic content in anthers. Meanwhile, both anthers and pollen extracts exhibited antioxidant activity, antibacterial activity, α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitory activity. In general, the anther stage of S4 showed the highest biological activity among all samples. This study illuminated the metabolites and biological activities of anthers and pollen of P. ostii, which supports the further utilization of them.
Keywords: Paeonia ostii; anther; biological activity; pollen; untargeted metabolomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Antioxidant Activities and Chemical Constituents of Flavonoids from the Flower of Paeonia ostii.Molecules. 2016 Dec 23;22(1):5. doi: 10.3390/molecules22010005. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 28025554 Free PMC article.
-
New insights on the analysis of phytosterols in pollen and anther wall of tree peony (Paeonia ostii 'Fengdan') revealed by GC-MS/MS.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 Jun 15;1212:339891. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.339891. Epub 2022 May 2. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35623781
-
Comprehensive comparison of different parts of Paeonia ostii, a food-medicine plant, based on untargeted metabolomics, quantitative analysis, and bioactivity analysis.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Aug 29;14:1243724. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1243724. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37711307 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of isolation methods of tomato pollen on the results of metabolic profiling.Metabolomics. 2019 Jan 8;15(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s11306-018-1471-4. Metabolomics. 2019. PMID: 30830456 Free PMC article.
-
Genus Paeonia: A comprehensive review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, clinical application, and toxicology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113708. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113708. Epub 2020 Dec 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33346027 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant and Tyrosinase-Inhibitory Activities and Biological Bioactivities of Flavonoid Derivatives from Quercus mongolica Pollen.Molecules. 2025 Feb 8;30(4):794. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040794. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005106 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Role of miR-211 in Health and Disease.Biomolecules. 2025 Aug 1;15(8):1109. doi: 10.3390/biom15081109. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40867554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen F., Zhang X., Du X., Yang L., Zu Y., Yang F. A New Approach for Obtaining Trans-Resveratrol from Tree Peony Seed Oil Extracted Residues Using Ionic Liquid-Based Enzymatic Hydrolysis in Situ Extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016;170:294–305. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2016.06.056. - DOI
-
- Cheng Y., Quan W., He Y., Qu T., Wang Z., Zeng M., Qin F., Chen J., He Z. Effects of Postharvest Irradiation and Su-perfine Grinding Wall Disruption Treatment on the Bioactive Compounds, Endogenous Enzyme Activities, and Antioxidant Properties of Pine (Pinus yunnanensis) Pollen during Accelerated Storage. LWT. 2021;144:111249. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111249. - DOI
-
- Alseekh S., Aharoni A., Brotman Y., Contrepois K., D’Auria J., Ewald J., Ewald J.C., Fraser P.D., Giavalisco P., Hall R.D., et al. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics: A Guide for Annotation, Quantification and Best Reporting Practices. Nat. Methods. 2021;18:747–756. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01197-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

