Transcriptome Analysis Elucidates the Potential Key Genes Involved in Rib Development in bmp6-Deficient Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix)
- PMID: 38791669
- PMCID: PMC11117292
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14101451
Transcriptome Analysis Elucidates the Potential Key Genes Involved in Rib Development in bmp6-Deficient Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix)
Abstract
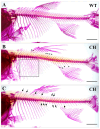
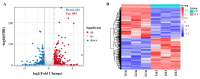
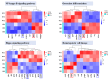
Bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP-6) is a constituent of the TGF-β superfamily, known for its ability to stimulate bone and cartilage formation. The investigation of bmp6's involvement in the formation of intermuscular bones in fish has garnered significant attention in recent years. The rib cage is an important skeletal structure that plays a protective function for internal organs in fish. However, there has been limited research conducted on the effects of the bmp6 gene on rib development. Silver carp is one of four major fish in China, favoured for its affordability and tender muscle. Nevertheless, the presence of numerous intermuscular bones in silver carp significantly hinders the advancement of its palatability and suitability for processing. This study showcases the effective utilisation of CRISPR/Cas9 technology for the purpose of disrupting the bmp6 gene in silver carp, leading to the creation of chimeras in the P0 generation, marking the first instance of such an achievement. The chimeras exhibited complete viability, normal appearance, and partial intermuscular bones loss, with approximately 30% of them displaying rib bifurcation or bending. Subsequently, a transcriptome analysis on ribs of P0 chimeras and wild-type silver carp was conducted, leading to the identification of 934 genes exhibiting differential expression, of which 483 were found to be up-regulated and 451 were found to be down-regulated. The results of the KEGG analysis revealed that the "NF-kappa B signalling pathway", "Hippo signalling pathway", "osteoclast differentiation", and "haematopoietic cell lineage" exhibited enrichment and displayed a significant correlation with bone development. The up-regulated genes such as tnfα, fos, and ctgf in pathways may facilitate the proliferation and differentiation of osteoclasts, whereas the down-regulation of genes such as tgfb2 and tgfbr1 in pathways may hinder the formation and specialisation of osteoblasts, ultimately resulting in rib abnormalities. This study presents novel findings on the impact of bmp6 gene deletion on the rib development of silver carp, while simultaneously investigating the previously unexplored molecular mechanisms underlying rib defects in fish.
Keywords: Hypophthalmichthys molitrix; bmp6; rib; transcriptome analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Nie C., Hilsdorf A.W.S., Wan S.-M., Gao Z.X. Understanding the development of intermuscular bones in teleost: Status and future directions for aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2020;12:759–772. doi: 10.1111/raq.12348. - DOI
-
- Dasilao J.C., Sasaki K., Okamura O. The hemiramphid, Oxyporhamphus, is a flyingfish (exocoetidae) Ichthyol. Res. 1997;44:101–107. doi: 10.1007/BF02678688. - DOI
-
- Fraser M.R., Anderson T.A., de Nys R. Ontogenic development of the spine and spinal deformities in larval barramundi (Lates calcarifer) culture. Aquaculture. 2004;242:697–711. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.09.018. - DOI
Grants and funding
- CARS-45/the earmarked fund for CARS
- 2023YFD2400303/National Key Research and Development Program
- 2022YFD2400100/National Key Research and Development Program
- 2023XT0402/Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS
- 2020TD36/Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

