Air Quality Monitoring Using Low-Cost Sensors in Urban Areas of Jodhpur, Rajasthan
- PMID: 38791837
- PMCID: PMC11120845
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph21050623
Air Quality Monitoring Using Low-Cost Sensors in Urban Areas of Jodhpur, Rajasthan
Abstract
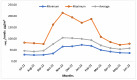
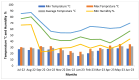
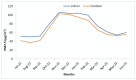
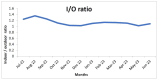
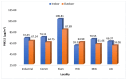
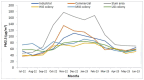
Air pollution poses a significant health hazard in urban areas across the globe, with India being one of the most affected countries. This paper presents environmental monitoring study conducted in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India, to assess air quality in diverse urban environments. The study involved continuous indoor and outdoor air quality monitoring, focusing on particulate matter (PM2.5) levels, bioaerosols, and associated meteorological parameters. Laser sensor-based low-cost air quality monitors were utilized to monitor air quality and Anderson 6-stage Cascade Impactor & Petri Dish methods for bioaerosol monitoring. The study revealed that PM2.5 levels were consistently high throughout the year, highlighting the severity of air pollution in the region. Notably, indoor PM2.5 levels were often higher than outdoor levels, challenging the common notion of staying indoors during peak pollution. The study explored the spatial and temporal diversity of air pollution across various land-use patterns within the city, emphasizing the need for tailored interventions in different urban areas. Additionally, bioaerosol assessments unveiled the presence of pathogenic organisms in indoor and outdoor environments, posing health risks to residents. These findings underscore the importance of addressing particulate matter and bioaerosols in air quality management strategies. Despite the study's valuable insights, limitations, such as using low-cost air quality sensors and the need for long-term data collection, are acknowledged. Nevertheless, this research contributes to a better understanding of urban air quality dynamics and the importance of public awareness in mitigating the adverse effects of air pollution. In conclusion, this study underscores the urgent need for effective air quality management strategies in urban areas. The findings provide valuable insights for policymakers and researchers striving to address air pollution in rapidly urbanizing regions.
Keywords: PM2.5; air pollution; ambient air quality; indoor air quality; microorganisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Behera M., Nath J., Pandey S., Boopathy R., Das T. Air Quality and Health. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2022. Pathogenicity, Characterisation and Impact of Ambient Bio-Aerosols on the Climatic Processes: With a Special Emphasis on the Indian Subcontinent.
-
- Ding W., Li L., Han Y., Liu J., Liu J. Site-related and seasonal variation of bioaerosol emission in an indoor wastewater treatment station: Level, characteristics of particle size, and microbial structure. Aerobiologia. 2016;32:211–224. doi: 10.1007/s10453-015-9391-5. - DOI
-
- Balyan P., Ghosh C., Das S., Banerjee B.D. Spatial variation of biogenic aerosols at different land use configurations in urban Delhi. Int. J. Appl. Environ. Sci. 2017;12:731–744.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

