Pepsinogen C Interacts with IQGAP1 to Inhibit the Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells by Suppressing Rho-GTPase Pathway
- PMID: 38791874
- PMCID: PMC11120368
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16101796
Pepsinogen C Interacts with IQGAP1 to Inhibit the Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells by Suppressing Rho-GTPase Pathway
Abstract
Aim: This study systematically explored the biological effects and mechanisms of PGC on gastric cancer (GC) cells in vitro and in vivo.
Method: The critical biological roles of PGC in GC were assessed via EdU staining, Hoechst staining, flow cytometry, mouse models, CCK-8, wound healing, transwell, and sphere-forming assays. The interaction study with IQ-domain GTPase-activating protein 1 (IQGAP1) was used by Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry co-immunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence staining, CHX-chase assay, MG132 assay, and qRT-PCR.
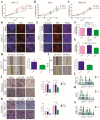
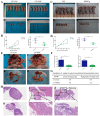
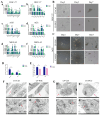
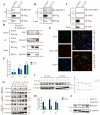
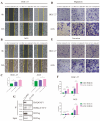
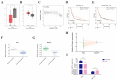
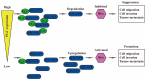
Results: PGC inhibited the proliferation, viability, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, invasion, and stemness of GC cells and promoted GC cell differentiation. PGC suppressed subcutaneous tumor growth and peritoneal dissemination in vivo. The interaction study found PGC inhibits GC cell migration and invasion by downregulating IQGAP1 protein and IQGAP1-mediated Rho-GTPase signaling suppression. In addition, PGC disrupts the stability of the IQGAP1 protein, promoting its degradation and significantly shortening its half-life. Moreover, the expression levels of PGC and IQGAP1 in GC tissues were significantly negatively correlated.
Conclusion: PGC may act as a tumor suppressor in the development and metastasis of GC. PGC can downregulate its interacting protein IQGAP1 and inhibit the Rho-GTPase pathway, thereby participating in the inhibition of GC cell migration and invasion.
Keywords: IQGAP1; biological behavior; gastric cancer; pepsinogen C; tumor metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

