Integrated Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Analysis of Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathway in Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua
- PMID: 38792110
- PMCID: PMC11124200
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29102248
Integrated Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Analysis of Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathway in Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua
Abstract
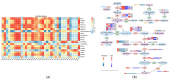
Flavonoids, a class of phenolic compounds, are one of the main functional components and have a wide range of molecular structures and biological activities in Polygonatum. A few of them, including homoisoflavonoids, chalcones, isoflavones, and flavones, were identified in Polygonatum and displayed a wide range of powerful biological activities, such as anti-cancer, anti-viral, and blood sugar regulation. However, few studies have systematically been published on the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Therefore, in the present study, a combined transcriptome and metabolome analysis was performed on the leaf, stem, rhizome, and root tissues of P. cyrtonema to uncover the synthesis pathway of flavonoids and to identify key regulatory genes. Flavonoid-targeted metabolomics detected a total of 65 active substances from four different tissues, among which 49 substances were first study to identify in Polygonatum, and 38 substances were flavonoids. A total of 19 differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) (five flavonols, three flavones, two dihydrochalcones, two flavanones, one flavanol, five phenylpropanoids, and one coumarin) were finally screened by KEGG enrichment analysis. Transcriptome analysis indicated that a total of 222 unigenes encoding 28 enzymes were annotated into three flavonoid biosynthesis pathways, which were "phenylpropanoid biosynthesis", "flavonoid biosynthesis", and "flavone and flavonol biosynthesis". The combined analysis of the metabolome and transcriptome revealed that 37 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) encoding 11 enzymes (C4H, PAL, 4CL, CHS, CHI, F3H, DFR, LAR, ANR, FNS, FLS) and 19 DAMs were more likely to be regulated in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway. The expression of 11 DEGs was validated by qRT-PCR, resulting in good agreement with the RNA-Seq. Our studies provide a theoretical basis for further elucidating the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in Polygonatum.
Keywords: Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua; differential metabolites; flavonoid biosynthesis; qRT-PCR; transcriptomics–metabolomics combined analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combined Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Analysis of the Distribution of Flavonoids in the Fibrous Root and Taproot of Polygonatum kingianum Coll.et Hemsl.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jun 22;15(7):828. doi: 10.3390/genes15070828. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062607 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analyses of metabolome and transcriptome reveal the dynamic accumulation and regulatory network in rhizomes and fruits of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 19;25(1):706. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10608-4. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39030489 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathway Involved in Rhizome Development in Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua.Plants (Basel). 2024 May 31;13(11):1524. doi: 10.3390/plants13111524. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891332 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic analysis of flavonoid diversity and biosynthetic pathways in whole grains.Food Res Int. 2025 Jun;211:116359. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116359. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Food Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40356159 Review.
-
Flavonoids from the genus Polygonatum: biological activities and biosynthesis mechanism.Front Nutr. 2025 Apr 10;12:1574182. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1574182. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40276535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoids as key players in cold tolerance: molecular insights and applications in horticultural crops.Hortic Res. 2025 Jan 2;12(4):uhae366. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae366. eCollection 2025 Apr. Hortic Res. 2025. PMID: 40070400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang W.W., Xia L., Peng F., Song C., Manzoor M.A., Cai Y., Jin Q. Transcriptomics and metabolomics changes triggered by exogenous 6-benzylaminopurine in relieving epicotyl dormancy of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua seeds. Front. Plant Sci. 2022;13:961899. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.961899. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tao A.E., Zhang X.C., Du Z.F., Zhao F.Y., Xia C.L., Duan B.Z. Research progress on flavonoids in plants of Polygonatum Mill. and their pharmacological activities. Chin. Tradi. Herb. Drugs. 2018;49:2163–2171. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.09.029. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

