Extraction and Biological Activity of Lignanoids from Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E.H.Wilson Residual Waste Biomass Using Deep Eutectic Solvents
- PMID: 38792212
- PMCID: PMC11124428
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29102352
Extraction and Biological Activity of Lignanoids from Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E.H.Wilson Residual Waste Biomass Using Deep Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
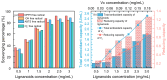
Lignanoids are an active ingredient exerting powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in the treatment of many diseases. In order to improve the efficiency of the resource utilization of traditional Chinese medicine waste, Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E.H.Wilson residue (MOR) waste biomass was used as raw material in this study, and a series of deep eutectic solvents (ChUre, ChAce, ChPro, ChCit, ChOxa, ChMal, ChLac, ChLev, ChGly and ChEG) were selected to evaluate the extraction efficiency of lignanoids from MORs. The results showed that the best conditions for lignanoid extraction were a liquid-solid ratio of 40.50 mL/g, an HBD-HBA ratio of 2.06, a water percentage of 29.3%, an extract temperature of 337.65 K, and a time of 107 min. Under these conditions, the maximum lignanoid amount was 39.18 mg/g. In addition, the kinetics of the extraction process were investigated by mathematic modeling. In our antioxidant activity study, high antioxidant activity of the lignanoid extract was shown in scavenging four different types of free radicals (DPPH, ·OH, ABTS, and superoxide anions). At a concentration of 3 mg/mL, the total antioxidant capacity of the lignanoid extract was 1.795 U/mL, which was equal to 0.12 mg/mL of Vc solution. Furthermore, the antibacterial activity study found that the lignanoid extract exhibited good antibacterial effects against six tested pathogens. Among them, Staphylococcus aureus exerted the strongest antibacterial activity. Eventually, the correlation of the lignanoid extract with the biological activity and physicochemical properties of DESs is described using a heatmap, along with the evaluation of the in vitro hypoglycemic, in vitro hypolipidemic, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory activity of the lignanoid extract. These findings can provide a theoretical foundation for the extraction of high-value components from waste biomass by deep eutectic solvents, as well as highlighting its specific significance in natural product development and utilization.
Keywords: biological activity; deep eutectic solvents; honokiol; magnolol; natural product extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Extraction and Purification of Aucubin from Eucommia ulmoides Seed Draff in Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Using Macroporous Resins.ACS Omega. 2023 Dec 29;9(1):1723-1737. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08332. eCollection 2024 Jan 9. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38222590 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of a Deep Eutectic Solvent and Macroporous Resin for Green Recovery of Iridoids, Chlorogenic Acid, and Flavonoids from Eucommia ulmoides Leaves.Molecules. 2024 Feb 5;29(3):737. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030737. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338480 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) as Alternative Sustainable Media for the Extraction and Characterization of Bioactive Compounds from Winemaking Industry Wastes.Molecules. 2025 Apr 21;30(8):1855. doi: 10.3390/molecules30081855. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40333869 Free PMC article.
-
Biological activity and toxicity of the Chinese herb Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E. Wilson (Houpo) and its constituents.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017 Mar.;18(3):194-214. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600299. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017. PMID: 28271656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green and sustainable extraction of lignin by deep eutectic solvent, its antioxidant activity, and applications in the food industry.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(20):7201-7219. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2181762. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36815260 Review.
References
-
- Ma H., Li H., Zhang F., Wang Q., Tu M. Effects of nitrogen substitute and Hypericum perforatum extract on the ethanol fermentation of traditional Chinese medicine dregs. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019;128:385–390. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.11.021. - DOI
-
- Woumbo C.Y., Kuate D., Klang M.J., Womeni H.M., Feregrino-Perez A.A. Valorization of Glycine max (Soybean) Seed Waste: Optimization of the Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE) and Characterization of Polyphenols from Soybean Meal Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) J. Chem. 2021;2021:4869909. doi: 10.1155/2021/4869909. - DOI
-
- Fontana R., Mattioli L.B., Biotti G., Budriesi R., Gotti R., Micucci M., Corazza I., Marconi P., Frosini M., Manfredini S., et al. Magnolia officinalis L. bark extract and respiratory diseases: From traditional Chinese medicine to western medicine via network target. Phytother. Res. 2023;37:2915. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7786. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

