Effectiveness of a Dual-Task Intervention Involving Exercise and Vocalized Cognitive Tasks
- PMID: 38792503
- PMCID: PMC11122377
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13102962
Effectiveness of a Dual-Task Intervention Involving Exercise and Vocalized Cognitive Tasks
Abstract
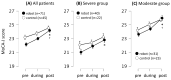
Background/Objectives: Population aging is rapidly increasing, and the importance of preventive medicine has been stressed. Health checkups, diet, and exercise are of paramount importance. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a personalized dual-task intervention that combined exercise with cognitive tasks in improving physical and cognitive functions among independently living older individuals. Methods: Participants aged >65 years who were mostly independent in their activities of daily living were divided into two groups. The group receiving the 20 min robot-assisted session was compared with the group receiving traditional functional restoration training. This randomized trial assessed the impact of this intervention on the 30 s chair stand test score and Montreal Cognitive Assessment-Japanese version score of the participants. Results: Both scores significantly improved in the intervention group, indicating enhanced lower-limb function and cognitive capabilities. Conclusions: These findings suggest that integrating cognitive tasks with physical exercise can stand as an effective strategy to improve overall well-being in older people, offering valuable insights for designing comprehensive preventive health programs tailored to this demographic.
Keywords: CS-30; MoCA-J; cross-step training; dual task.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Director-General for Statistics, Information System Management and Industrial Relations Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Government of Japan . Abridged Life Tables for Japan 2022. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare; Tokyo, Japan: 2022. pp. 1–9.
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare . Vital Statistics. e-Stat; Tokyo, Japan: 2021.
-
- Gates N., Fiatarone Singh M.A., Sachdev P.S., Valenzuela M. The effect of exercise training on cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry. 2013;21:1086–1097. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2013.02.018. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

