Intracellular Host Restriction of Hepatitis B Virus Replication
- PMID: 38793645
- PMCID: PMC11125714
- DOI: 10.3390/v16050764
Intracellular Host Restriction of Hepatitis B Virus Replication
Abstract
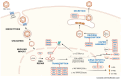
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) infects hepatocytes and hijacks host cellular mechanisms for its replication. Host proteins can be frontline effectors of the cell's defense and restrict viral replication by impeding multiple steps during its intracellular lifecycle. This review summarizes many of the well-described restriction factors, their mechanisms of restriction, and counteractive measures of HBV, with a special focus on viral transcription. We discuss some of the limitations and knowledge gaps about the restriction factors, highlighting how these factors may be harnessed to facilitate therapeutic strategies against HBV.
Keywords: Smc5/6; cccDNA transcriptional silencing; hepatitis B virus; host restriction factors; viral transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mueller S.N., Rouse B.T. Host defenses to viruses. Clin. Immunol. 2013;2013:346–355.
-
- Dunn C., Peppa D., Khanna P., Nebbia G., Jones M., Brendish N., Lascar R.M., Brown D., Gilson R.J., Tedder R.J., et al. Temporal Analysis of Early Immune Responses in Patients With Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:1289–1300. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.06.054. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang Z., Trippler M., Real C.I., Werner M., Luo X., Schefczyk S., Kemper T., Anastasiou O.E., Ladiges Y., Treckmann J., et al. Hepatitis B Virus Particles Activate Toll-Like Receptor 2 Signaling Initially Upon Infection of Primary Human Hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2020;72:829–844. doi: 10.1002/hep.31112. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sato S., Li K., Kameyama T., Hayashi T., Ishida Y., Murakami S., Watanabe T., Iijima S., Sakurai Y., Watashi K., et al. The RNA Sensor RIG-I Dually Functions as an Innate Sensor and Direct Antiviral Factor for Hepatitis B Virus. Immunity. 2014;42:123–132. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.12.016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

