Dual-Message QR Codes
- PMID: 38793911
- PMCID: PMC11124860
- DOI: 10.3390/s24103055
Dual-Message QR Codes
Abstract
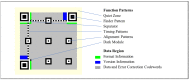
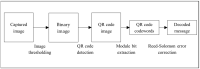
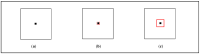
A novel dual-message QR code is proposed for carrying two individual messages that can be read by standard QR code readers: one from a close range and the other from a large distance. By exploring the module value determining the rule of typical QR code readers, we designed two-state module blocks that can be recognized as different module values through changing the distance from which the QR code is scanned, and applied them to construct the proposed dual-message QR code. Experiments were conducted to test the readability of the two messages within a dual-message QR code, with the results demonstrating the high feasibility of the proposed method. The dual-message QR code can be applied for designing creative applications. For example, an interactive wedding card that can access the growing film of the groom and that of the bride interchangeably, which bring the viewers a higher-quality experience.
Keywords: 2D barcode; QR code; dual-message QR code; nested QR code; two-layer QR code.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Information Technology—Automatic Identification and Data Capture Techniques—QR Code Bar Code Symbology Specification. ISO/IEC; Genève, Switzerland: 2015.
-
- Tiwari S. An introduction to QR code technology; Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT); Bhubaneswar, India. 22–24 December 2016; pp. 39–44.
-
- Belussi L.F.F., Hirata N.S.T. Fast QR code detection in arbitrarily acquired images; Proceedings of the 2011 24th SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images; Alagoas, Brazil. 28–31 August 2011; pp. 281–288.
-
- Lin J.A., Fuh C.S. 2D barcode image decoding. Math. Prob. Eng. 2013;2013:848276. doi: 10.1155/2013/848276. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

