Characterization, Biocompatibility and Antioxidant Activity of Hydrogels Containing Propolis Extract as an Alternative Treatment in Wound Healing
- PMID: 38794145
- PMCID: PMC11123975
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17050575
Characterization, Biocompatibility and Antioxidant Activity of Hydrogels Containing Propolis Extract as an Alternative Treatment in Wound Healing
Abstract
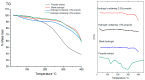
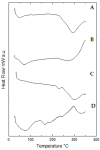
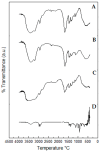
Hydrogels consist of a network of highly porous polymeric chains with the potential for use as a wound dressing. Propolis is a natural product with several biological properties including anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antioxidant activities. This study was aimed at synthesizing and characterizing a polyacrylamide/methylcellulose hydrogel containing propolis as an active ingredient, to serve as a wound dressing alternative, for the treatment of skin lesions. The hydrogels were prepared using free radical polymerization, and were characterized using scanning electron microscopy, infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetry, differential scanning calorimetry, swelling capacity, mechanical and rheological properties, UV-Vis spectroscopy, antioxidant activity by the DPPH, ABTS and FRAP assays and biocompatibility determined in Vero cells and J774 macrophages by the MTT assay. Hydrogels showed a porous and foliaceous structure with a well-defined network, a good ability to absorb water and aqueous solutions simulating body fluids as well as desirable mechanical properties and pseudoplastic behavior. In hydrogels containing 1.0 and 2.5% propolis, the contents of total polyphenols were 24.74 ± 1.71 mg GAE/g and 32.10 ± 1.01 mg GAE/g and those of total flavonoids 8.01 ± 0.99 mg QE/g and 13.81 ± 0.71 mg QE/g, respectively, in addition to good antioxidant activity determined with all three methods used. Therefore, hydrogels containing propolis extract, may serve as a promising alternative wound dressing for the treatment of skin lesions, due to their anti-oxidant properties, low cost and availability.
Keywords: Apis mellifera; cytotoxicity; dressing; hydrogel; natural product; propolis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Hydrogel Containing Propolis: Physical Characterization and Evaluation of Biological Activities for Potential Use in the Treatment of Skin Lesions.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 20;17(10):1400. doi: 10.3390/ph17101400. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459039 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial polysaccharide-based hydrogel dressing containing plant essential oil for burn wound healing.Burns Trauma. 2021 Dec 22;9:tkab041. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkab041. eCollection 2021. Burns Trauma. 2021. PMID: 34988231 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of arginine-NIPAAm hybrid hydrogel as wound dressing: In vitro and in vivo study.Acta Biomater. 2018 Jan;65:305-316. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.08.048. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 28867649
-
Potential use of propolis-loaded quaternized chitosan/pectin hydrogel films as wound dressings: Preparation, characterization, antibacterial evaluation, and in vitro healing assay.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jun 30;241:124633. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124633. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37119912
-
New Insights for Red Propolis of Alagoas-Chemical Constituents, Topical Membrane Formulations and Their Physicochemical and Biological Properties.Molecules. 2020 Dec 9;25(24):5811. doi: 10.3390/molecules25245811. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33317120 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biorefining Brazilian Green Propolis: An Eco-Friendly Approach Based on a Sequential High-Pressure Extraction for Recovering High-Added-Value Compounds.Molecules. 2025 Jan 6;30(1):189. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010189. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39795246 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogel Containing Propolis: Physical Characterization and Evaluation of Biological Activities for Potential Use in the Treatment of Skin Lesions.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 20;17(10):1400. doi: 10.3390/ph17101400. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459039 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy Study of Propolis Eutectic Extract in Gel Formulations for the Treatment of Bacterial Skin Diseases in Dogs.Animals (Basel). 2025 May 15;15(10):1434. doi: 10.3390/ani15101434. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajaz N., Abbas A., Afshan R., Irfan M., Khalid S.H., Asghar S., Munir M.U., Rizg W.Y., Majrashi K.A., Alshehri S., et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin-grafted-poly(acrylic acid)/poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) semi-interpenetrating matrices of dexamethasone sodium phosphate. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15:1399. doi: 10.3390/ph15111399. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

