Lipid Nanoparticles in Lung Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 38794306
- PMCID: PMC11124812
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050644
Lipid Nanoparticles in Lung Cancer Therapy
Abstract
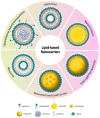
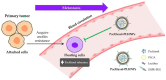
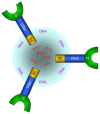
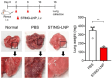
This manuscript explores the use of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) in addressing the pivotal challenges of lung cancer treatment, including drug delivery inefficacy and multi-drug resistance. LNPs have significantly advanced targeted therapy by improving the precision and reducing the systemic toxicity of chemotherapeutics such as doxorubicin and paclitaxel. This manuscript details the design and benefits of various LNP systems, including solid lipid-polymer hybrids, which offer controlled release and enhanced drug encapsulation. Despite achievements in reducing tumor size and enhancing survival, challenges such as manufacturing complexity, biocompatibility, and variable clinical outcomes persist. Future directions are aimed at refining targeting capabilities, expanding combinatorial therapies, and integrating advanced manufacturing techniques to tailor treatments to individual patient profiles, thus promising to transform lung cancer therapy through interdisciplinary collaboration and regulatory innovation.
Keywords: drug delivery; drug resistance; lipid nanoparticles; lung cancer; personalized medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of Interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advanced Targeted Therapy for Colorectal Cancer with Lipid Nanoparticles.Curr Med Chem. 2025 Jan 16. doi: 10.2174/0109298673327576241201145252. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39819540
-
Chemistry of Lipid Nanoparticles for RNA Delivery.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Jan 4;55(1):2-12. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00544. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 34850635 Review.
-
A landscape of recent advances in lipid nanoparticles and their translational potential for the treatment of solid tumors.Bioeng Transl Med. 2023 Nov 9;9(2):e10601. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10601. eCollection 2024 Mar. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38435821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review on lipid nanocarrier systems for cancer treatment: fabrication, future prospects and clinical trials.J Liposome Res. 2024 Mar;34(1):135-177. doi: 10.1080/08982104.2023.2204372. Epub 2023 May 5. J Liposome Res. 2024. PMID: 37144339 Review.
-
Developing Biodegradable Lipid Nanoparticles for Intracellular mRNA Delivery and Genome Editing.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Nov 2;54(21):4001-4011. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00500. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34668716 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of lipid-based nanoparticles in the management of oral squamous cell carcinoma.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024;5(6):1223-1246. doi: 10.37349/etat.2024.00272. Epub 2024 Sep 29. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024. PMID: 39465011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart nanomedicines powered by artificial intelligence: a breakthrough in lung cancer diagnosis and treatment.Med Oncol. 2025 Mar 25;42(5):134. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02680-x. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40131617 Review.
-
Global research trends and emerging hotspots in nano-drug delivery systems for lung cancer: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis (1998-2024).Discov Oncol. 2025 Jan 11;16(1):33. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01782-2. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39798040 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Chondroitin Sulfate-Based Nanoplatforms for Biomedical Applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Aug 9;20:9857-9881. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S533559. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40808714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NIR-Responsive Microbubble Delivery Platforms for Controlled Drug Release in Cancer Therapy.Materials (Basel). 2025 Jun 10;18(12):2725. doi: 10.3390/ma18122725. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40572858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pramual S., Lirdprapamongkol K., Jouan-Hureaux V., Barberi-Heyob M., Frochot C., Svasti J., Niamsiri N. Overcoming the diverse mechanisms of multidrug resistance in lung cancer cells by photodynamic therapy using pTHPP-loaded PLGA-lipid hybrid nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020;149:218–228. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.02.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang Y., Huang Z., Li J., Mo Z., Huang Y., Ma C., Wang W., Pan X., Wu C. PLGA Porous Microspheres Dry Powders for Codelivery of Afatinib-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Paclitaxel: Novel Therapy for EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Resistant Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019;8:e1900965. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201900965. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liang Y., Tian B., Zhang J., Li K., Wang L., Han J., Wu Z. Tumor-targeted polymeric nanostructured lipid carriers with precise ratiometric control over dual-drug loading for combination therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017;12:1699–1715. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S121262. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu C., Xu J., Hao Y., Zhao Y., Qiu Y., Jiang J., Yu T., Ji P., Liu Y. Application of a lipid-coated hollow calcium phosphate nanoparticle in synergistic co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel for the treatment of human lung cancer A549 cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017;12:7979–7992. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S140957. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu R., Zhang Z., Wang B., Chen G., Zhang Y., Deng H., Tang Z., Mao J., Wang L. Combination Chemotherapy of Lung Cancer—Co-Delivery of Docetaxel Prodrug and Cisplatin Using Aptamer-Decorated Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020;14:2249–2261. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S246574. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

