Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with early breast cancer
- PMID: 38796284
- PMCID: PMC11145753
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.102974
Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with early breast cancer
Abstract
The European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Clinical Practice Guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with early breast cancer were updated and published online in 2023, and adapted, according to previously established standard methodology, to produce the Pan-Asian adapted (PAGA) ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of Asian patients with early breast cancer. The adapted guidelines presented in this manuscript represent the consensus opinions reached by a panel of Asian experts in the treatment of patients with breast cancer representing the oncological societies of China (CSCO), Indonesia (ISHMO), India (ISMPO), Japan (JSMO), Korea (KSMO), Malaysia (MOS), the Philippines (PSMO), Singapore (SSO), Taiwan (TOS) and Thailand (TSCO), co-ordinated by ESMO and KSMO. The voting was based on scientific evidence and was independent of the current treatment practices, drug access restrictions and reimbursement decisions in the different Asian regions represented by the 10 oncological societies. The latter are discussed separately in the manuscript. The aim is to provide guidance for the optimisation and harmonisation of the management of patients with early breast cancer across the different regions of Asia, drawing on the evidence provided by both Western and Asian trials, whilst respecting the differences in screening practices, molecular profiling, as well as the age and stage at presentation. Attention is drawn to the disparity in the drug approvals and reimbursement strategies, between the different regions of Asia.
Keywords: ESMO; Pan-Asian; early breast cancer; guidelines; treatment.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
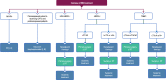
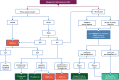
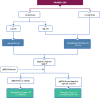
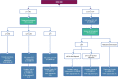
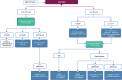
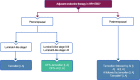
References
-
- Ferlay J., Ervik M., Lam F., et al., editors. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2020. https://gco.iarc.fr/ Available at.
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Ottini L., Palli D., Rizzo S., et al. Male breast cancer. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol. 2010;73(2):141–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

