Effect of DPP-4i inhibitors on renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 38796440
- PMCID: PMC11128128
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-024-02132-x
Effect of DPP-4i inhibitors on renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Aims: About 20-40% patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) had an increased risk of developing diabetic nephropathy (DN). Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4i) were recommended for treatment of T2DM, while the impact of DPP-4i on renal function remained unclear. This study aimed to explore the effect of DPP-4i on renal parameter of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) in T2DM.
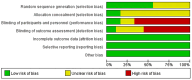
Methods: A systematic search was performed across PubMed, Embase and Cochrane Library. A fixed or random-effects model was used for quantitative synthesis according to the heterogeneity, which was assessed with I2 index. Sensitivity analysis and publication bias were performed with standard methods, respectively.
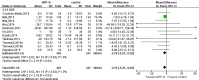
Results: A total of 17 randomized controlled trials were identified. Administration of DPP-4i produced no significant effect on eGFR (WMD, -0.92 mL/min/1.73m2, 95% CI, -2.04 to 0.19) in diabetic condition. DPP-4i produced a favorable effect on attenuating ACR (WMD, -2.76 mg/g, 95% CI, -5.23 to -0.29) in patients with T2DM. The pooled estimate was stable based on the sensitivity test. No publication bias was observed according to Begg's and Egger's tests.
Conclusions: Treatment with DPP-4i preserved the renal parameter of eGFR in diabetic condition. Available evidences suggested that administration of DPP-4i produced a favorable effect on attenuating ACR in patients with T2DM. INTERNATIONAL PROSPECTIVE REGISTER FOR SYSTEMATIC REVIEW (PROSPERO) NUMBER: CRD.42020144642.
Keywords: Albumin-to-creatinine ratio; Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors; Estimated glomerular filtration rate; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous