Analysis of online prescription patterns in Chinese patients with sequelae of cerebral infarction: a real-world study
- PMID: 38796623
- PMCID: PMC11127947
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-62923-1
Analysis of online prescription patterns in Chinese patients with sequelae of cerebral infarction: a real-world study
Abstract
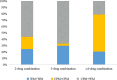
Cerebral infarction (CI) is a common cerebrovascular disease worldwide, and the burden caused by the sequelae of CI has increased significantly. However, current treatment guidelines lack standardized recommendations for pharmacotherapy of sequelae of CI. This retrospective study collected and analyzed 1.98 million prescriptions concerning sequelae of CI from patients admitted to Zhiyun Health Internet Hospital in 2022. The mean age of patients was 66.2 ± 11.4 years, and 52.40% were male. 79.73% had one or more comorbidities. For treatment, the prescriptions of 1-, 2- and ≥ 3-drug accounted for 64.55%, 23.77% and 11.68% respectively. Chinese patent medicine (CPM) prescriptions, western medicine (WM) prescriptions, and CPM and WM combined (CPM + WM) prescriptions accounted for 53.81%, 27.33%, and 18.86% respectively. In CPM prescriptions, the most frequently prescribed medications were Salvia miltiorrhiza (34.81%), Ginkgo biloba (24.96%), Panax notoginseng (20.67%), Gastrodia (7.15%) and Ligusticum Wallichii (4.90%). For WM prescriptions, the most commonly prescribed agents were anti-hypertensive (32.82%), anti-thrombotic (16.06%), vasodilator (15.70%), anti-dementia (10.88%), and lipid-lowering (9.58%) drugs. Among CPM + WM prescriptions, 72.61% had CPM/WM = 1, 21.20% had CPM/WM < 1, and 6.19% had CPM/WM > 1. This research utilized real-world data extracted from internet hospitals in China to present valuable evidence of online prescription patterns among patients experiencing sequelae of CI.
Keywords: Chinese patent medicine; Prescription pattern; Real-world data; Sequelae of cerebral infarction; Western medicine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescribing characteristics and guideline concordance of antihypertensive western and Chinese patent medicine in Internet hospitals in China: a cross-sectional study.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1580787. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1580787. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40371350 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of combined Chinese medicine and Western medicine for ischemic stroke patients.Chin J Integr Med. 2014 Aug;20(8):570-84. doi: 10.1007/s11655-014-1759-9. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Chin J Integr Med. 2014. PMID: 25087603
-
[Study on clinical characteristics of Danshen Chuanxiongqin Injection in treatment of cerebral infarction in real world].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Jul;45(14):3307-3315. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200327.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32726044 Chinese.
-
Effects and Perspectives of Chinese Patent Medicines for Tonifying Qi and Promoting Blood Circulation on Patients with Cerebral Infarction.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2015;13(4):475-91. doi: 10.2174/1570161112666141014150232. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25360841 Review.
-
Several considerations in using traditional Chinese patent medicine for cerebral infarction.Chin J Integr Med. 2012 Aug;18(8):571-4. doi: 10.1007/s11655-012-1186-8. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Chin J Integr Med. 2012. PMID: 22855032 Review.
Cited by
-
Prescribing characteristics and guideline concordance of antihypertensive western and Chinese patent medicine in Internet hospitals in China: a cross-sectional study.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1580787. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1580787. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40371350 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

