CEACAM6 expression and function in tumor biology: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 38796667
- PMCID: PMC11127906
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01053-6
CEACAM6 expression and function in tumor biology: a comprehensive review
Abstract
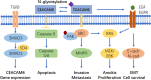
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) is an immunoglobulin superfamily protein primarily expressed on epithelial surfaces and myeloid cells. It plays a significant role in cancer progression by inhibiting apoptosis, promoting drug resistance, and facilitating cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Overexpression of CEACAM6 has been observed in various cancers, including lung, breast, colorectal, and hepatocellular cancers, and is associated with poorer overall survival and disease-free survival. Its differential expression on tumor cell surfaces makes it a promising cancer marker. This review aims to provide a comprehensive summary of CEACAM6's role in different cancer types, its involvement in signaling pathways, and recent advancements in CEACAM6-targeted treatments.
Keywords: Biomarkers; CEACAM6; TME; Therapeutic target; Vaccine therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Towards understanding the mechanisms of actions of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 in cancer progression.Cancer Sci. 2018 Jan;109(1):33-42. doi: 10.1111/cas.13437. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29110374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CEACAM6's Role as a Chemoresistance and Prognostic Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer: A Comparison of CEACAM6's Diagnostic and Prognostic Capabilities with Those of CA19-9 and CEA.Life (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;11(6):542. doi: 10.3390/life11060542. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207784 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role and Targeting of Carcinoembryonic Antigen-related Cell Adhesion Molecule 6 (CEACAM6) in Human Malignancies.Clin Cancer Drugs. 2015 Feb;2(2):100-111. doi: 10.2174/2212697X02666150602215823. Clin Cancer Drugs. 2015. PMID: 27595061 Free PMC article.
-
CEACAM6 promotes cholangiocarcinoma migration and invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of the SRC/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jan;23(1):39. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13157. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 34966455 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging roles of CEACAM6 in human cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Mar;64(3):27. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5615. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38240103 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and biological evaluation of a novel CEACAM6-targeted PET tracer for distinguishing malignant nodules in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Jun;52(7):2414-2430. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07107-3. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39888423
-
The influence of hypoxia-mediated CEACAM6 upregulation on epithelial cell and macrophage response in the context of gastric cancer.Eur J Clin Invest. 2024 Dec;54 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):e14352. doi: 10.1111/eci.14352. Eur J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39674878 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Genetic Screening on the Syndromes of Colorectal Cancer and Gastric Cancer: A 2024 Update.Biomedicines. 2024 Nov 21;12(12):2655. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122655. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767561 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schölzel S, Zimmermann W, Schwarzkopf G, et al. Carcinoembryonic antigen family members CEACAM6 and CEACAM7 are differentially expressed in normal tissues and oppositely deregulated in hyperplastic colorectal polyps and early adenomas. Am J Pathol. 2000;156(2):595–605. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64764-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources