Optimizing esthetic zone periodontal regeneration in a 1-2-wall infrabony defect using recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor BB and β-tricalcium phosphate: A case report
- PMID: 38798052
- PMCID: PMC11128747
- DOI: 10.1002/cre2.908
Optimizing esthetic zone periodontal regeneration in a 1-2-wall infrabony defect using recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor BB and β-tricalcium phosphate: A case report
Abstract
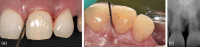
Objective: Periodontitis is an inflammatory condition induced by subgingival bacterial dysbiosis, resulting in inflammatory-mediated destruction of tooth-supporting structures, potentially leading to the formation of infrabony defects. This case report describes the treatment of a patient who presented with a combination 1-2-wall defect on tooth 21. To maintain the residual periodontal attachment and minimize esthetic consequences, a regenerative approach was performed using recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB (rh-PDGF-BB) and β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP).
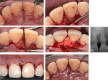
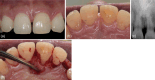
Materials and methods: At the time of postscaling/root planing reevaluation, a 34-year-old Asian male initially diagnosed with molar/incisor pattern stage III grade C periodontitis exhibited a 6-mm residual probing depth on the mesiopalatal aspect of tooth 21. Periodontal regenerative surgery was performed using rh-PDGF-BB with β-TCP, without the use of a membrane.
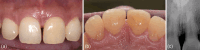
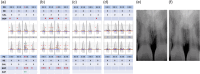
Results: At the 1-year follow-up, a significant reduction in probing depth and radiographic evidence of bone fill were observed. Additionally, re-entry surgery for implant placement at site tooth 23 confirmed bone fill in the defect on tooth 21.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate the efficacy of rh-PDGF-BB with β-TCP in enhancing periodontal regeneration and support its use as a treatment option when treating poorly contained infrabony defects in the esthetic zone.
Keywords: biologic; case report; periodontal regeneration; platelet‐derived growth factor.
© 2024 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Artzi, Z. , Weinreb, M. , Givol, N. , Rohrer, M. D. , Nemcovsky, C. E. , Prasad, H. S. , & Tal, H. (2004). Biomaterial resorption rate and healing site morphology of inorganic bovine bone and beta‐tricalcium phosphate in the canine: A 24‐month longitudinal histologic study and morphometric analysis. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, 19(3), 357–368. - PubMed
-
- Avila‐Ortiz, G. , Ambruster, J. , Barootchi, S. , Chambrone, L. , Chen, C. Y. , Dixon, D. R. , Geisinger, M. L. , Giannobile, W. V. , Goss, K. , Gunsolley, J. C. , Heard, R. H. , Kim, D. M. , Mandelaris, G. A. , Monje, A. , Nevins, M. L. , Palaiologou‐Gallis, A. , Rosen, P. S. , Scheyer, E. T. , Suarez‐Lopez del Amo, F. , … Mealey, B. L. (2022). American Academy of Periodontology best evidence consensus statement on the use of biologics in clinical practice. Journal of Periodontology, 93(12), 1763–1770. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cortellini, P. , Prato, G. P. , & Tonetti, M. S. (1993). Periodontal regeneration of human infrabony defects. II. Re‐entry procedures and bone measures. Journal of Periodontology, 64(4), 261–268. - PubMed
-
- Darby, I. B. , & Morris, K. H. (2013). A systematic review of the use of growth factors in human periodontal regeneration. Journal of Periodontology, 84(4), 465–476. - PubMed
-
- Eke, P. I. , Dye, B. A. , Wei, L. , Slade, G. D. , Thornton‐Evans, G. O. , Borgnakke, W. S. , Taylor, G. W. , Page, R. C. , Beck, J. D. , & Genco, R. J. (2015). Update on prevalence of periodontitis in adults in the United States: NHANES 2009 to 2012. Journal of Periodontology, 86(5), 611–622. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

