Antimicrobial resistance and associated risk factors in Escherichia coli isolated from Peruvian dogs: A focus on extended-spectrum β-lactamases and colistin
- PMID: 38798292
- PMCID: PMC11111722
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.880-887
Antimicrobial resistance and associated risk factors in Escherichia coli isolated from Peruvian dogs: A focus on extended-spectrum β-lactamases and colistin
Abstract
Background and aim: Established antimicrobial resistance (AMR) surveillance in companion animals is lacking, particularly in low-middle-income countries. The aim of this study was to analyze AMR and its risk factors in Escherichia coli isolated from dogs at two veterinary centers in Lima (Peru).
Materials and methods: Ninety dogs were included in the study. Antimicrobial susceptibility was established by disk diffusion, whereas microdilution was used to determine colistin susceptibility. Mechanisms related to extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL) and colistin resistance were determined by polymerase chain reaction. Clonal relationships of colistin-resistant isolates were assessed by XbaI-pulsed-field gel electrophoresis.
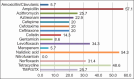
Results: Thirty-five E. coli strains were isolated. High levels of resistance to ampicillin (57.1%), nalidixic acid (54.3%), tetracycline (48.6%), and azithromycin (25.7%) were detected. Cephalosporin resistance levels were ≥20% and those for colistin were 14.3%. Twelve (34.2%) isolates were ESBL producers; of these, six blaCTX-M-55 (50.0%), 2 (16.6%) blaCTX-M-15, and 2 (16.6%) blaCTX-M-8-like genes were found. The five colistin-resistant isolates were clonally unrelated, with four of them presenting amino acid codon substitutions in the mgrB gene (V8A) or mutations in the mgrB promoter (a12g, g98t, and c89t). Furthermore, dog age, <6 years (p = 0.027) and raw diet (p = 0.054) were associated with resistance to a greater number of antibiotic families.
Conclusion: Despite small number of samples included, the study found that dogs studied were carriers of multidrug-resistant E. coli, including last-resort antimicrobials, representing a public health problem due to close contact between dogs and humans. This issue suggests the need for larger studies addressed to design strategies to prevent the spread of resistant micro-organisms in small animal clinics and domestic settings.
Keywords: Peru; antibiotic resistance; colistin; dogs; extended-spectrum β-lactamases; risk factor.
Copyright: © Ventura, et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Guardabassi L, Schwarz S, Lloyd D.H. Pet animals as reservoirs of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004;54(2):321–332. - PubMed
-
- Ramos C.P, Kamei C.Y.I, Viegas F.M, de Melo Barbieri J, Cunha J.L.R, Hounmanou Y.M.G, Coura F.M, Santana J.A, Lobato F.C.F, Bojesen A.M, Silva R.O.S. Fecal shedding of multidrug resistant Escherichia coli isolates in dogs fed with raw meat-based diets in Brazil. Antibiotics. 2022;11(4):534. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carvalho I, Carvalho J.A, Martinez-Alvarez S, Sadi M, Capita R, Alonso-Calleja C, Rabbi F, Dapkevicius M.L.N, Igrejas G, Torres C, Poeta P. Characterization of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from clinical samples in a Northern Portuguese hospital:Predominance of CTX-M-15 and high genetic diversity. Microorganisms. 2021;9(9):1914. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources