This is a preprint.
Structural insights into GrpEL1-mediated nucleotide and substrate release of human mitochondrial Hsp70
- PMID: 38798347
- PMCID: PMC11118385
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.10.593630
Structural insights into GrpEL1-mediated nucleotide and substrate release of human mitochondrial Hsp70
Update in
-
Structural insights into GrpEL1-mediated nucleotide and substrate release of human mitochondrial Hsp70.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 30;15(1):10815. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54499-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39737924 Free PMC article.
Abstract
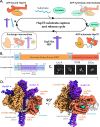
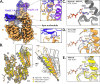
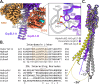
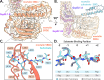
Maintenance of protein homeostasis is necessary for cell viability and depends on a complex network of chaperones and co-chaperones, including the heat-shock protein 70 (Hsp70) system. In human mitochondria, mitochondrial Hsp70 (mortalin) and the nucleotide exchange factor (GrpEL1) work synergistically to stabilize proteins, assemble protein complexes, and facilitate protein import. However, our understanding of the molecular mechanisms guiding these processes is hampered by limited structural information. To elucidate these mechanistic details, we used cryoEM to determine the first structures of full-length human mortalin-GrpEL1 complexes in previously unobserved states. Our structures and molecular dynamics simulations allow us to delineate specific roles for mortalin-GrpEL1 interfaces and to identify steps in GrpEL1-mediated nucleotide and substrate release by mortalin. Subsequent analyses reveal conserved mechanisms across bacteria and mammals and facilitate a complete understanding of sequential nucleotide and substrate release for the Hsp70 chaperone system.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics Declaration The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
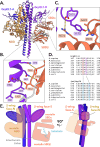
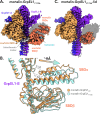

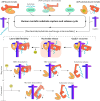
References
-
- Kim Y. E.; Hipp M. S.; Bracher A.; Hayer-Hartl M.; Ul-rich Hartl F. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 323–355. - PubMed
-
- Voos W. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 2013, 1833, 388–399. - PubMed
-
- Morán Luengo T.; Mayer M. P.; Rüdiger S. G. Trends in Cell Biology 2019, 29, 164–177. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
