This is a preprint.
Control of Inflammatory Response by Tissue Microenvironment
- PMID: 38798655
- PMCID: PMC11118380
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.10.592432
Control of Inflammatory Response by Tissue Microenvironment
Abstract
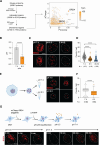
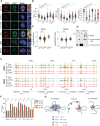
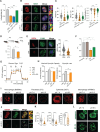
Inflammation is an essential defense response but operates at the cost of normal tissue functions. Whether and how the negative impact of inflammation is monitored remains largely unknown. Acidification of the tissue microenvironment is associated with inflammation. Here we investigated whether macrophages sense tissue acidification to adjust inflammatory responses. We found that acidic pH restructured the inflammatory response of macrophages in a gene-specific manner. We identified mammalian BRD4 as a novel intracellular pH sensor. Acidic pH disrupts the transcription condensates containing BRD4 and MED1, via histidine-enriched intrinsically disordered regions. Crucially, a decrease in macrophage intracellular pH is necessary and sufficient to regulate transcriptional condensates in vitro and in vivo, acting as negative feedback to regulate the inflammatory response. Collectively, these findings uncovered a pH-dependent switch in transcriptional condensates that enables environment-dependent control of inflammation, with a broader implication for calibrating the magnitude and quality of inflammation by the inflammatory cost.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.C.K. consults and holds equity in Corner Therapeutics and Larkspur Biosciences. None of these relationships impacted this study. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
