Phytochemical constituents analysis in laminaria digitata for Alzheimer's disease: molecular docking and in-silico toxicity approach
- PMID: 38798825
- PMCID: PMC11123516
- DOI: 10.1080/19420889.2024.2357346
Phytochemical constituents analysis in laminaria digitata for Alzheimer's disease: molecular docking and in-silico toxicity approach
Abstract
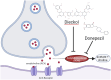
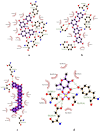
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a common brain disease associated with cognitive impairment and dementia. donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor drug as a commercial AD drug represents a non-cost-effective treatment with the toxic effects reported. As the prevalence of AD increases, the development of effective therapeutic treatments is urgently required. Laminaria digitata is a brown seaweed claimed to be able to prevent and treat neurodegenerative diseases. Therefore, this study measured and compared the binding affinity and toxicity of seven common phytoconstituents in Laminaria digitata against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) with those of donepezil using a molecular docking approach. The binding free energy values of donepezil, dieckol, eckol, fucodiphlorethol G, 7-Phloroecol, laminaran, alginic acid, and fucoidan with acetylcholinesterase (AChE) were -12.3, -13.5, -10.5, -8,7, -9.7, -8.0, -10.3, and -7.4 kcal/mol. All ligands constantly interacted with the AChE amino acid residues, namely Tyr124. Dieckol, with the strongest and most stable interaction, is classified as class IV toxicity, with an LD50 value of 866 mg/kg. It has aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) toxicity at certain doses. Theoretically, based on Lipinski's rule, dieckol is likely to have poor absorption and permeation properties; therefore, several considerations during the drug discovery process are needed.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase inhibition; Alzheimer; Laminaria digitata; docking molecular.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring Medicinal Herbs' Therapeutic Potential and Molecular Docking Analysis for Compounds as Potential Inhibitors of Human Acetylcholinesterase in Alzheimer's Disease Treatment.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 12;59(10):1812. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101812. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893530 Free PMC article.
-
De-novo Drug Design, Molecular Docking and In-Silico Molecular Prediction of AChEI Analogues through CADD Approaches as Anti-Alzheimer's Agents.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2020;16(1):54-72. doi: 10.2174/1573409915666190301124210. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2020. PMID: 30827255 Free PMC article.
-
6-Methyluracil derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015;27 Suppl 1:S69-71. doi: 10.3233/JRS-150694. Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015. PMID: 26639718
-
Acetylcholinesterase Enzyme Inhibitor Molecules with Therapeutic Potential for Alzheimer's Disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2022;21(5):427-449. doi: 10.2174/1871527320666210928160159. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 34602041 Review.
-
Multi-Target Directed Donepezil-Like Ligands for Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2016 May 25;10:205. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00205. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27252617 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Marine-derived polysaccharides: the potential agents against neurodegenerative diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 18;15:1506789. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1506789. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39744139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
