Unveiling the gut-eye axis: how microbial metabolites influence ocular health and disease
- PMID: 38799150
- PMCID: PMC11122920
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1377186
Unveiling the gut-eye axis: how microbial metabolites influence ocular health and disease
Abstract
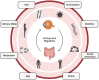
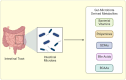
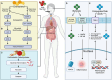
The intricate interplay between the gut microbiota and ocular health has surpassed conventional medical beliefs, fundamentally reshaping our understanding of organ interconnectivity. This review investigates into the intricate relationship between gut microbiota-derived metabolites and their consequential impact on ocular health and disease pathogenesis. By examining the role of specific metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate and bile acids (BAs), herein we elucidate their significant contributions to ocular pathologies, thought-provoking the traditional belief of organ sterility, particularly in the field of ophthalmology. Highlighting the dynamic nature of the gut microbiota and its profound influence on ocular health, this review underlines the necessity of comprehending the complex workings of the gut-eye axis, an emerging field of science ready for further exploration and scrutiny. While acknowledging the therapeutic promise in manipulating the gut microbiome and its metabolites, the available literature advocates for a targeted, precise approach. Instead of broad interventions, it emphasizes the potential of exploiting specific microbiome-related metabolites as a focused strategy. This targeted approach compared to a precision tool rather than a broad-spectrum solution, aims to explore the therapeutic applications of microbiome-related metabolites in the context of various retinal diseases. By proposing a nuanced strategy targeted at specific microbial metabolites, this review suggests that addressing specific deficiencies or imbalances through microbiome-related metabolites might yield expedited and pronounced outcomes in systemic health, extending to the eye. This focused strategy holds the potential in bypassing the irregularity associated with manipulating microbes themselves, paving a more efficient pathway toward desired outcomes in optimizing gut health and its implications for retinal diseases.
Keywords: bile acids; butyrate; microbiome; ocular diseases; short chain fatty acids.
Copyright © 2024 Nguyen, Rudd Zhong Manis, Ronczkowski, Bui, Oxenrider, Jadeja and Thounaojam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

