Lysosomal degradation of PD-L1 is associated with immune-related adverse events during anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in NSCLC patients
- PMID: 38799168
- PMCID: PMC11116720
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1384733
Lysosomal degradation of PD-L1 is associated with immune-related adverse events during anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in NSCLC patients
Abstract
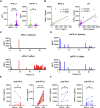
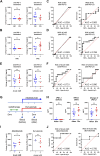
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) can induce immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Liquid biomarkers to predict irAE occurrence are urgently needed. We previously developed an ELISA system to specifically detect soluble PD-L1 (sPD-L1) with PD-1-binding capacity (bsPD-L1). Here, we investigated the relationship between sPD-L1 and bsPD-L1 in gastric cancer (GC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade and their association with irAEs. Methods: We examined sPD-L1, bsPD-L1, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and proinflammatory cytokine levels by ELISA in plasma samples from 117 GC patients prior to surgery and 72 NSCLC patients prior to and at 2 months after ICI treatment (anti-PD-1, n = 48; anti-PD-L1, n = 24). In mice treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies (Abs), sPD-L1 levels and localization of Abs were examined by ELISA and immunohistochemistry, respectively. Results:sPD-L1 was detected with higher frequency in GC patients than in NSCLC patients, whereas bsPD-L1 was detected with similar frequencies in GC and NSCLC patients. sPD-L1 levels were correlated with IL-1α, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 levels, while bsPD-L1 levels were correlated with MMP13, MMP3, and IFN-γ levels. In NSCLC patients, anti-PD-L1, but not anti-PD-1, treatment increased sPD-L1, which was associated with irAE development, but not with clinical outcomes. In mice, trafficking of anti-PD-L1 Abs to lysosomes in F4/80+ macrophages resulted in sPD-L1 production, which was suppressed by treatment with lysosomal degradation inhibitor chloroquine and macrophage depletion. Conclusion: Anti-PD-L1-mediated lysosomal degradation induces sPD-L1 production, which can serve as an indicator to predict irAE development during anti-PD-L1 treatment.
Keywords: immune-related adverse event; inflammation; lysosomal degradation; macrophage; soluble PD-L1.
Copyright © 2024 Kashiwada, Takano, Ando, Kuroda, Miyabe, Owada, Miyanaga, Asatsuma-Okumura, Hashiguchi, Kanazawa, Yoshida, Seike, Gemma and Iwai.
Conflict of interest statement
YI has patent applications for immunopotentiating compositions (WO/2009/0297518, 2011/0081341, 2014/0314714, 2015/0093380, 2015/0197572, 2016/0158356, 2016/0158355, 2017/0051060, and 2020/0062846) and an immune function evaluation method (WO/2019/049974). YI reports research grants from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JP19K07783 and JP22K07262 to YI) and Sysmex Corporation. AG reports consulting fees from MSD, Nippon Kayaku, and Daiichi-Sankyo Company outside the submitted work. MS reports receiving research grants from Taiho Pharmaceutical, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Nippon Kayaku, and Kyowa Hakko Kirin and honoraria from AstraZeneca, MSD, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Novartis, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Nippon Kayaku, Daiichi-Sankyo Company, Merck Biopharma, and Amgen outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Ando F., Kashiwada T., Kuroda S., Fujii T., Takano R., Miyabe Y., et al. (Forthcoming 2024). Combination of plasma MMPs and PD-1-binding soluble PD-L1 predicts recurrence in gastric cancer and the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Pharmacol. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Durand I., Alberti L., Bendriss-Vermare N., Valladeau-Guilemond J., Duc A., et al. (2016). A novel regulation of PD-1 ligands on mesenchymal stromal cells through MMP-mediated proteolytic cleavage. Oncoimmunology 5 (3), e1091146. 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1091146 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

