Review of facial acanthosis nigricans: Easy to diagnose and difficult to treat marker of hyperinsulinemia/metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 38799993
- PMCID: PMC11117019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2024.04.011
Review of facial acanthosis nigricans: Easy to diagnose and difficult to treat marker of hyperinsulinemia/metabolic syndrome
Abstract
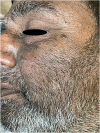
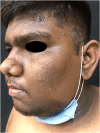
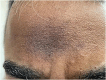
Facial acanthosis nigricans (FAN) is an increasingly discussed anatomical variation of acanthosis nigricans (AN). Its presentation as brown to black pigmentation with ill-defined blurred margins with varying degree of textural changes commonly over forehead, temporal, and malar regions of the face predominantly in dark-skinned individuals with a male predilection can be confused with other common facial melanoses. Its pathogenesis, clinical features, and management are in many ways similar to in the commonly described areas like neck and major flexural areas. Understanding of FAN has gained momentum in the past decade with studies highlighting its association with various metabolic abnormalities particularly insulin resistance and obesity. It is now being considered to be a cutaneous marker of metabolic syndrome. While there is uniformity in its clinical description, there appears to be scope for further in depth biochemical and histopathological studies to link the pigmentation, altered texture and microscopic changes in individuals presenting with FAN and hyperinsulinemia with or without other features of metabolic syndrome. It awaits a consensus on grading its severity and correlating it with histological features as patients often hesitate to be subjected to a biopsy of the face. This is a review of current literature pertaining to FAN. Newer clinical, dermoscopic, histopathological, and biochemical insights will help to understand this relatively new entity.
Keywords: Acanthosis nigricans; Facial acanthosis nigricans; HOMA-IR; Insulin resistance; Metformin.
© 2024 Director General, Armed Forces Medical Services. Published by Elsevier, a division of RELX India Pvt. Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have none to declare.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Clinico-investigative Study of Facial Acanthosis Nigricans.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2022 Mar 3;13(2):221-228. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_855_20. eCollection 2022 Mar-Apr. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2022. PMID: 35287408 Free PMC article.
-
A descriptive study of facial acanthosis nigricans and its association with body mass index, waist circumference and insulin resistance using HOMA2 IR.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016 Nov-Dec;7(6):498-503. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.193898. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016. PMID: 27990384 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of Metabolic Syndrome in Acanthosis Nigricans - A Hospital Based Cross-Sectional Study.Indian J Dermatol. 2022 Jan-Feb;67(1):92. doi: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_442_21. Indian J Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35656279 Free PMC article.
-
Acanthosis Nigricans: An Updated Review.Curr Pediatr Rev. 2022;19(1):68-82. doi: 10.2174/1573396318666220429085231. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2022. PMID: 36698243 Review.
-
Hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, and acanthosis nigricans syndrome: a common endocrinopathy with distinct pathophysiologic features.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Sep 1;147(1):90-101. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(83)90091-1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983. PMID: 6351620 Review.
Cited by
-
Global hotspots and trends in Acanthosis nigricans research: A bibliometric and visualized analysis.Skin Res Technol. 2024 Sep;30(9):e70054. doi: 10.1111/srt.70054. Skin Res Technol. 2024. PMID: 39258800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khalifa Sharquie P.E., Adil Noaimi P.A., Al-Ogaily S.M. Acanthosis nigricans as a cause of facial M Elanosis (Clinical Andhistopathological Study) IOSR J Dent Med Sci Ver IV. 2015;14(7):2279–2861.
-
- Barabash-Neila R., Freire L.R.F., Zulueta-Dorado T., Conejo-Mir J. Thickening of the skin on the forehead: a quiz. Acanthosis nigricans with forehead location. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91(1):1–2. - PubMed
-
- Sharquie K.E., Noaimi A.A., Mahmood H.G., Al-Ogaily S.M. Clinical and biochemical evaluation of facial acanthosis nigricans. J Cosmet Dermatological Sci Appl. 2015;5(3):231–237.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

