SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in Canadian blood donors: Insight into donor representativeness of the general population
- PMID: 38800670
- PMCID: PMC11127215
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2024.100498
SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in Canadian blood donors: Insight into donor representativeness of the general population
Abstract
Introduction: Blood donors world-wide were indispensable for monitoring anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies generated by infection and vaccination during the pandemic. Prior to the pandemic, donor vaccination behaviours were under-studied. We aimed to compare the percentage of Canadian blood donors with SARS-CoV-2 vaccination antibodies with the percentage of the general population who received at least one dose of vaccine each month during initial vaccine deployment. We also report donor attitudes towards SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.
Methods: Canadian blood donors were randomly selected for SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing over 2021 (N = 165,240). The percentage of donor samples with vaccination antibodies were compared with the percentage of general population who received at least one dose of vaccine in each month of 2021 except February. A random sample of Canadian blood donors were surveyed about vaccination intent and attitudes (N = 4,558 participated, 30.4 % response rate).
Results: The percentages of the general population vaccinated and donors with vaccination antibodies increased from 1 % to over 90 %. General population vaccination was greater early in vaccine deployment than donors (p < 0.05), greater in donors than the general population by mid-2021 (p < 0.05) but they were similar by the end of 2021. While 52.6 % of surveyed donors had received vaccine in May 2021, a further 41.1 % intended to when eligible. Most donors thought COVID-19 infection could be serious (83.5 %) and that it was important to be vaccinated even if previously infected (77.8 %).
Conclusion: Early pandemic vaccine prioritization to at-risk individuals and healthcare workers gave rise to higher general population vaccination percentages, while donors had higher vaccine antibody percentages as vaccine was deployed to progressively younger age groups. Since blood donors may be more willing to receive vaccination, under pandemic conditions they may be valuable for monitoring vaccination-induced seroprevalence.
Keywords: Blood donors; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Vaccination.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Chantale Pambrun reports financial support was provided by Government of Canada. Steven Drews reports equipment, drugs, or supplies was provided by Abbott Laboratories. Steven Drews reports a relationship with F Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd that includes.
Figures
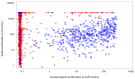
 vaccinated and unvaccinated blood donors in March 2021
vaccinated and unvaccinated blood donors in March 2021  . Note: As it takes up to 2 weeks to develop antibodies, donors who were recently vaccinated may have low or no anti-S.
. Note: As it takes up to 2 weeks to develop antibodies, donors who were recently vaccinated may have low or no anti-S.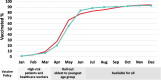
 compared with the percentage of blood donors aged 18–69 with vaccine antibodies (Anti-S positive but anti-N negative)
compared with the percentage of blood donors aged 18–69 with vaccine antibodies (Anti-S positive but anti-N negative)  .
.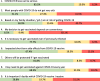
 Agreed
Agreed  Undecided
Undecided  Disagree.
Disagree.Similar articles
-
Changing Patterns of SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence among Canadian Blood Donors during the Vaccine Era.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0033922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00339-22. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35412385 Free PMC article.
-
Booster vaccinations and Omicron: the effects on SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in Dutch blood donors.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Jul 12;23(1):464. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08448-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37438703 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in Nova Scotia blood donors.J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis Can. 2024 Mar 29;9(1):32-45. doi: 10.3138/jammi-2023-0017. eCollection 2024 Mar. J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis Can. 2024. PMID: 38567363 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of COVID-19 Seropositive Plasma as Convalescent Plasma: An Immune and Neutralization Antibody Seroprevalence Analysis in Blood Donors for Future Potential Pandemic Readiness.Cureus. 2024 Mar 28;16(3):e57149. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57149. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38681329 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody among SARS-CoV-2 vaccinated vs post-infected blood donors in a tertiary hospital, Bangkok, Thailand.PLoS One. 2023 May 18;18(5):e0285737. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285737. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37200273 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Influenza and COVID-19 vaccination in Canadian blood donors: A comparison across pre- and post-pandemic periods.Vox Sang. 2025 May;120(5):464-472. doi: 10.1111/vox.70006. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Vox Sang. 2025. PMID: 40015315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vermeulen M., Swanevelder R., Van Zyl G., Lelie N., Murphy E.L. An assessment of hepatitis B virus prevalence in South African young blood donors born after the implementation of the infant hepatitis B virus immunization program: Implications for transfusion safety. Transfusion. 2021;61:2688–2700. doi: 10.1111/trf.16559. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

