Nomograms based on ratio indexes to predict severity and prognosis in immune checkpoint inhibitors-related myocarditis: a retrospective analysis
- PMID: 38801421
- PMCID: PMC11602797
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-024-05801-7
Nomograms based on ratio indexes to predict severity and prognosis in immune checkpoint inhibitors-related myocarditis: a retrospective analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Nomograms based on ratio indexes to predict severity and prognosis in immune checkpoint inhibitors-related myocarditis: a retrospective analysis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Feb 11;151(2):74. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06110-3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39932565 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: Immune checkpoint inhibitors-related myocarditis (ICI-M) is one of the immune-related adverse events (irAEs), which is rare and highly lethal. This study aimed to establish nomograms based on ratio biomarkers to predict the severity and prognosis of ICI-M.
Methods: We retrospectively examined patients with advanced cancers who were also diagnosed with ICI-M at the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University. The patients of ICI-M were divided into mild and severe groups and a 40-day following up was carried out. The major adverse cardiovascular events(MACEs) were regarded as the endpoint. Nomogram-based models were established and validated.
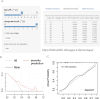
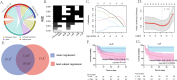
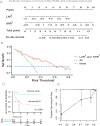
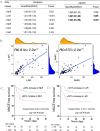
Results: Seventy-seven patients were involved, including 31 severe cases(40.3%). Lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio(LAR) combined with the change rate from baseline to onset of LAR( LAR) which performed best to diagnose the severe ICI-M was identified to establish the nomogram-based model. The bootstrap-corrected concordance index [0.752 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.635 0.866] and calibration plot with good degree of fitting confirmed this diagnostic model. Neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio(NHR) and LAR were also screened into the nomogram-based model for 40-day MACEs after ICI-M, which performed well by validating for concordance index(0.779 95% CI: 0.677 0.865)and calibration plots after being bootstrap-corrected. Moreover, a 101% increase in LAR significantly separated patients in MACE-free survival.
Conclusion: Ratio indexes at onset and their change rates from baseline showed good diagnostic value for the severity of ICI-M and prognostic value for subsequent MACEs, particularly LAR, NHR and their change rates. The nomogram-based models of ratio indexes could provide a potential choice for early detection and monitor of the severe ICI-M and subsequent MACEs.
Keywords: Diagnostic analysis; ICI-associated myocarditis; MACE; Nomogram; Predictive model; Prognostic analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Analysis of risk factors and establishment of prediction model for immune checkpoint inhibitor related myocarditis and major adverse cardiovascular events].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2024 Nov 24;52(11):1290-1295. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20231210-00489. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39557528 Chinese.
-
Development of peripheral biomarker-based prognostic nomograms for short-term and long-term survival in immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2025 Apr 30;15(2):277-290. doi: 10.21037/cdt-24-556. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2025. PMID: 40385270 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of inflammation and nutritional index in immunotherapy for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer and model construction.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 30;14(1):17511. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66813-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39080372 Free PMC article.
-
A review of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and biomarkers.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2512645. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2512645. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40505635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of high-dose steroids versus low-dose steroids in the treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis: a case series and systematic review.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 12;16:1455347. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1455347. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40013153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afzal MZ, Sarwar T, Shirai K (2019) Prognostic significance of hematological indices in malignant melanoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother 42(7):251–264. 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000272 - PubMed
-
- Cadour F, Cautela J, Rapacchi S, Varoquaux A, Habert P, Arnaud F, Jacquier A, Meilhac A, Paganelli F, Lalevee N, Scemama U, Thuny F (2022) Cardiac MRI features and prognostic value in immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced myocarditis. Radiology 303(3):512–521. 10.1148/radiol.211765 - PubMed
-
- Caforio AL, Pankuweit S, Arbustini E et al (2013) Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: a position statement of the european society of cardiology working group on myocardial and pericardial diseases. Eur Heart J 34(33):2636–2648. 10.1093/eurheartj/eht210. (2648a-2648d) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

