The value of urinary exosomal microRNA-21 in the early diagnosis and prognosis of bladder cancer
- PMID: 38801488
- PMCID: PMC11895653
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12845
The value of urinary exosomal microRNA-21 in the early diagnosis and prognosis of bladder cancer
Abstract
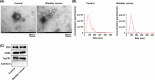
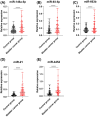
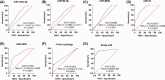
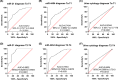
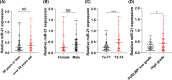
Bladder cancer (BC) poses high morbidity and mortality, with urinary exosomal microRNA (miR)-21 showing potential value in its diagnosis and prognosis, and we probed its specific role. We prospectively selected 116 BC patients and 116 healthy volunteers as the BC and control groups, respectively. BC urinary exosomal miR-146a-5p, miR-93-5p, miR-663b, miR-21, and miR-4454 relative expression levels were assessed. The correlations between clinical indexes and urinary exosomal miR-21, prognostic value of miR-21, and diagnostic value of the five candidate miRNAs, urine cytology, and miRNA joint diagnostic panel for BC and urinary exosomal miR-21, miR-4454, and urine cytology for Ta-T1 and T2-T4 stage BC were analyzed. Urinary exosomal miR-146a-5p, miR-93-5p, miR-663b, miR-21, and miR-4454 were highly expressed in BC patients. miR-146a-5p, miR-93-5p, miR-663b, miR-21, miR-4454, miRNA combined diagnostic panel, and urine cytology had certain diagnostic value for BC, with miR-21, miR-4454, and miRNA co-diagnostic panel showing the highest diagnostic value. Collectively, urinary exosomal miR-21 was closely related to Tumor-Node-Metastasis staging and grading in BC patients. Urinary exosomal miR-21 had high diagnostic value for BC and Ta-T1 and T2-T4 stage BC, and had high predictive value for BC poor prognosis, providing an effective indicator for the occurrence, development, and prognostic assessment of BC.
Keywords: bladder cancer; diagnosis; microRNA‐21; prognosis; urinary exosome.
© 2024 The Authors. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mi Y, Wang X. Comprehensive investigation of genes associated with cell cycle pathways for prognosis and immunotherapy in bladder urothelial carcinoma. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2022;41(3):1–12. - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi H, Duddalwar V, Daneshmand S. Diagnosis and staging of bladder cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2021;35(3):531–541. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

