Trends in cancer-related suicide in the United States: a population-based epidemiology study spanning 40 years of data
- PMID: 38802377
- PMCID: PMC11130301
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-024-02917-9
Trends in cancer-related suicide in the United States: a population-based epidemiology study spanning 40 years of data
Abstract
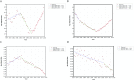
Large cohort studies examining trends in cancer-related suicide are lacking. We analyzed data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, encompassing a total of 4,870,410 patients diagnosed with cancer from 1975 to 2017 in the United States. Joinpoint regression was used to estimate the annual percent change (APC) and average annual percentage change (AAPC) of age-adjusted rates of suicide. In the past 40 years, we revealed a gradual increase in cancer-related suicide rates from 1975 to 1989, followed by a gradual decrease from 1989 to 2013, and a marked decrease from 2013 to 2017. These trends suggested the potential impact of advancements in psychosocial care for patients with cancer in contributing to the observed decrease in suicide rates.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- National Center for Injury Prevention and Control CfDCaP. National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), National Vital Statistics System. February 20, 2020.
-
- Hedegaard H, Curtin S, Warner M. Increase in Suicide Mortality in the United States, 1999-2018. NCHS data brief 2020: 1–8. - PubMed
-
- WISQARS C. Ten leading causes of death by age group. 2021.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

