A plasma protein-based risk score to predict hip fractures
- PMID: 38802582
- PMCID: PMC11333168
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-024-00639-7
A plasma protein-based risk score to predict hip fractures
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: A plasma protein-based risk score to predict hip fractures.Nat Aging. 2024 Oct;4(10):1508. doi: 10.1038/s43587-024-00717-w. Nat Aging. 2024. PMID: 39256542 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
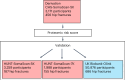
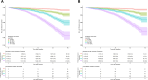
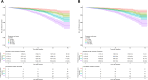
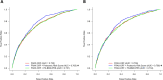
As there are effective treatments to reduce hip fractures, identification of patients at high risk of hip fracture is important to inform efficient intervention strategies. To obtain a new tool for hip fracture prediction, we developed a protein-based risk score in the Cardiovascular Health Study using an aptamer-based proteomic platform. The proteomic risk score predicted incident hip fractures and improved hip fracture discrimination in two Trøndelag Health Study validation cohorts using the same aptamer-based platform. When transferred to an antibody-based proteomic platform in a UK Biobank validation cohort, the proteomic risk score was strongly associated with hip fractures (hazard ratio per s.d. increase, 1.64; 95% confidence interval 1.53-1.77). The proteomic risk score, but not available polygenic risk scores for fractures or bone mineral density, improved the C-index beyond the fracture risk assessment tool (FRAX), which integrates information from clinical risk factors (C-index, FRAX 0.735 versus FRAX + proteomic risk score 0.776). The developed proteomic risk score constitutes a new tool for stratifying patients according to hip fracture risk; however, its improvement in hip fracture discrimination is modest and its clinical utility beyond FRAX with information on femoral neck bone mineral density remains to be determined.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
B.M.P. serves on the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson, which had no impact on this paper. J.B.R. is founder and CEO of 5 Prime Sciences, which provides research services for biotech, pharma and venture capital companies for projects unrelated to this research. T.L. is an employee of 5 Prime Sciences. J.B.R. has served as an advisor to GSK and Deerfield Capital. The institution of J.B.R. has received investigator-initiated grant funding from Eli Lilly, GSK and Biogen for projects unrelated to this research. J.R.K. reports stock ownership in Abbott, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, Medtronic, Merck and Pfizer. J.A.K. is a director of Osteoporosis Research, which maintains and develops FRAX. C.O. is an applicant on filed patent applications on the effect of probiotics on bone metabolism. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL130114/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL144483/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- U01HL080295/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- KAW 2015.0317/Knut och Alice Wallenbergs Stiftelse (Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation)
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- LU2021-0096/IngaBritt och Arne Lundbergs Forskningsstiftelse (Ingabritt and Arne Lundberg Research Foundation)
- 75N92021D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2020-01392/Vetenskapsrådet (Swedish Research Council)
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL144483/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

