Association of Life's Essential 8 with all-cause mortality and risk of cancer: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 38802806
- PMCID: PMC11129373
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-18879-y
Association of Life's Essential 8 with all-cause mortality and risk of cancer: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: No study has concentrated on the association of LE8 with cancer risk and death. We aim to examine the association of LE8 with death and cancer.
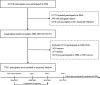
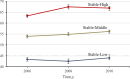
Methods: A total of 94733 adults aged 51.42 ± 12.46 years and 77551 participants aged 54.09±12.06 years were enrolled in longitudinal and trajectory analysis respectively. Baseline LE8 was divided into three groups based on the American Heart Association criteria and three trajectory patterns by latent mixture models. We reviewed medical records and clinical examinations to confirm incident cancer during the period from 2006 to 2020. Death information was collected from provincial vital statistics offices. Cox models were used.
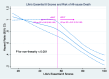
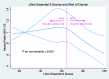
Results: 12807 all-cause deaths and 5060 cancers were documented during a 14-year follow-up. Relative to participants with high LE8 at baseline, participants with lower levels of LE8 have a significantly increased risk of mortality and incident cancer. All these risks have an increasing trend with LE8 level decreasing. Meanwhile, the trajectory analysis recorded 7483 all-cause deaths and 3037 incident cancers after approximately 10 years. The associations of LE8 with death and cancer were identical to the longitudinal study. In the subtype cancer analysis, LE8 has a strong effect on colorectal cancer risk. Moreover, the cut point is 56.67 in the association between LE8 and death, while the cut point altered to 64.79 in the association between LE8 and incident cancers. These associations were enhanced among younger adults.
Conclusions: There was a significant association of LE8 with death and cancer risk, especially for the young population.
Keywords: Cancer; Death; Life's essential 8; Longitudinal analysis; Threshold effect; Trajectory analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer IAfRo: Latest global cancer data: Cancer burden rises to 19.3 million new cases and 10.0 million cancer deaths in 2020. World Health Organization; 2020. https://www.iarc.who.int/news-events/latest-global-cancer-data-cancer-bu....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

