Association of deletion polymorphism rs10573247 in the HMGA2 gene with the risk of breast cancer: bioinformatic and experimental analyses
- PMID: 38802807
- PMCID: PMC11131319
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-024-03415-4
Association of deletion polymorphism rs10573247 in the HMGA2 gene with the risk of breast cancer: bioinformatic and experimental analyses
Abstract
Background: The high mobility group A2 (HMGA2) gene is expressed extensively during early embryonic development but is inactivated in adulthood, and it is also reactivated in various benign and malignant tumors, including breast cancer. We first assessed the potential functional significance of the unstudied deletion polymorphism rs10573247 at the 3'UTR of HMGA2 on miRNA binding using bioinformatic tools, and subsequently, the association between this polymorphism and breast cancer susceptibility was investigated.
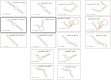
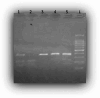
Materials and methods: We applied the RNAhybrid tool to predict the functional effects of polymorphism rs10573247 located within the 3' UTR of the HMGA2 gene on miRNA binding. Then, following DNA extraction, 141 breast cancer patients and 123 healthy controls were genotyped for polymorphism rs10573247 using RFLP-PCR with the restriction enzyme Eam1104I.
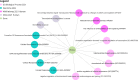
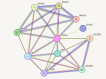
Results: Our bioinformatic data have shown that polymorphism rs10573247 is located in the region that serves as a potential target site for eight miRNAs binding. Among them, miR-3125 exhibited decreased binding affinity for the allele delTT (MFE = -21.8) when compared to the allele TT (MFE = -23.9), but miR-4476 increased binding affinity for the allele delTT (MFE = -22.4) compared to the allele TT (MFE = -22.2). In addition, our results showed that the genotype TT/delTT (p = 0.005) and the genotype delTT/delTT (p = 0.029) were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing breast cancer compared to the genotype TT/TT using RFLP-PCR.
Discussion and conclusion: Our findings suggest that polymorphism rs10573247 may contribute to the risk of breast cancer through the functional effect of this polymorphism on miRNA binding.
Keywords: Bioinformatic; Breast Cancer; Deletion polymorphism rs10573247; HMGA2; miR-3125; miR-4476.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

