A non-invasive preoperative prediction model for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer based on a machine learning approach: combining ultrasonographic parameters and breast gamma specific imaging features
- PMID: 38802938
- PMCID: PMC11131273
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-024-02453-2
A non-invasive preoperative prediction model for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer based on a machine learning approach: combining ultrasonographic parameters and breast gamma specific imaging features
Abstract
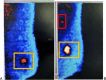
Background: The most common route of breast cancer metastasis is through the mammary lymphatic network. An accurate assessment of the axillary lymph node (ALN) burden before surgery can avoid unnecessary axillary surgery, consequently preventing surgical complications. In this study, we aimed to develop a non-invasive prediction model incorporating breast specific gamma image (BSGI) features and ultrasonographic parameters to assess axillary lymph node status.
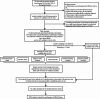
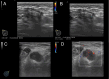
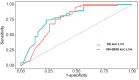
Materials and methods: Cohorts of breast cancer patients who underwent surgery between 2012 and 2021 were created (The training set included 1104 ultrasound images and 940 BSGI images from 235 patients, the test set included 568 ultrasound images and 296 BSGI images from 99 patients) for the development of the prediction model. six machine learning (ML) methods and recursive feature elimination were trained in the training set to create a strong prediction model. Based on the best-performing model, we created an online calculator that can make a linear predictor in patients easily accessible to clinicians. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and calibration curve are used to verify the model performance respectively and evaluate the clinical effectiveness of the model.
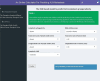
Results: Six ultrasonographic parameters (transverse diameter of tumour, longitudinal diameter of tumour, lymphatic echogenicity, transverse diameter of lymph nodes, longitudinal diameter of lymph nodes, lymphatic color Doppler flow imaging grade) and one BSGI features (axillary mass status) were selected based on the best-performing model. In the test set, the support vector machines' model showed the best predictive ability (AUC = 0.794, sensitivity = 0.641, specificity = 0.8, PPV = 0.676, NPV = 0.774 and accuracy = 0.737). An online calculator was established for clinicians to predict patients' risk of ALN metastasis ( https://wuqian.shinyapps.io/shinybsgi/ ). The result in ROC showed the model could benefit from incorporating BSGI feature.
Conclusion: This study developed a non-invasive prediction model that incorporates variables using ML method and serves to clinically predict ALN metastasis and help in selection of the appropriate treatment option.
Keywords: Axillary lymph node; Breast neoplasms; Breast specific gamma image; Machine learning; Ultrasonography.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Global Cancer S. 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. (2021);71(3):209–49. 10.3322/caac.21660 - PubMed
-
- Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB. Sentinel-lymph-node resection compared with conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in clinically node-negative patients with breast cancer: overall survival findings from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase 3 trial. LANCET ONCOL. 2010;11(10):927–33. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70207-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Donker M, van Tienhoven G, Straver ME. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer (EORTC 10981–22023 AMAROS): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. LANCET ONCOL. 2014;15(12):1303–10. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70460-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

