USP25 Elevates SHLD2-Mediated DNA Double-Strand Break Repair and Regulates Chemoresponse in Cancer
- PMID: 38803048
- PMCID: PMC11267380
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202403485
USP25 Elevates SHLD2-Mediated DNA Double-Strand Break Repair and Regulates Chemoresponse in Cancer
Abstract
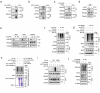
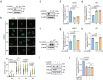
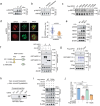
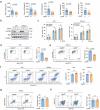
DNA damage plays a significant role in the tumorigenesis and progression of the disease. Abnormal DNA repair affects the therapy and prognosis of cancer. In this study, it is demonstrated that the deubiquitinase USP25 promotes non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), which in turn contributes to chemoresistance in cancer. It is shown that USP25 deubiquitinates SHLD2 at the K64 site, which enhances its binding with REV7 and promotes NHEJ. Furthermore, USP25 deficiency impairs NHEJ-mediated DNA repair and reduces class switch recombination (CSR) in USP25-deficient mice. USP25 is overexpressed in a subset of colon cancers. Depletion of USP25 sensitizes colon cancer cells to IR, 5-Fu, and cisplatin. TRIM25 is also identified, an E3 ligase, as the enzyme responsible for degrading USP25. Downregulation of TRIM25 leads to an increase in USP25 levels, which in turn induces chemoresistance in colon cancer cells. Finally, a peptide that disrupts the USP25-SHLD2 interaction is successfully identified, impairing NHEJ and increasing sensitivity to chemotherapy in PDX model. Overall, these findings reveal USP25 as a critical effector of SHLD2 in regulating the NHEJ repair pathway and suggest its potential as a therapeutic target for cancer therapy.
Keywords: DNA repair pathways; SHLD2; cancer therapy; deubiquitinase USP25; peptides.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
USP44 regulates irradiation-induced DNA double-strand break repair and suppresses tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 25;13(1):501. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28158-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35079021 Free PMC article.
-
SHLD2/FAM35A co-operates with REV7 to coordinate DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice.EMBO J. 2018 Sep 14;37(18):e100158. doi: 10.15252/embj.2018100158. Epub 2018 Aug 28. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 30154076 Free PMC article.
-
USP14 regulates DNA damage repair by targeting RNF168-dependent ubiquitination.Autophagy. 2018;14(11):1976-1990. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1496877. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29995557 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Trim25 in development, disease and RNA metabolism.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Aug 15;44(4):1045-50. doi: 10.1042/BST20160077. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27528750 Review.
-
Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice: a new focus on 53BP1.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021 Jan 15;22(1):38-46. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2000306. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021. PMID: 33448186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Katsuki Y., Jeggo P. A., Uchihara Y., Takata M., Shibata A., Genome Instab Dis. 2020, 1, 155.
-
- Dev H., Chiang T. W., Lescale C., de Krijger I., Martin A. G., Pilger D., Coates J., Sczaniecka‐Clift M., Wei W., Ostermaier M., Herzog M., Lam J., Shea A., Demir M., Wu Q., Yang F., Fu B., Lai Z., Balmus G., Belotserkovskaya R., Serra V., O'Connor M. J., Bruna A., Beli P., Pellegrini L., Caldas C., Deriano L., Jacobs J. J. L., Galanty Y., Jackson S. P., Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 954. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFA1302803/National Key Research and Development Plan
- 82225035/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32090032/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32070713/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81872298/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81802754/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22XD1422300/Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality
- 22120240382/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 22120230228/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 2022XD053/Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
