Paramedian Frontal Flap Reconstruction for Nasal Defect Following an Accidental Amputation
- PMID: 38803405
- PMCID: PMC11129609
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.61167
Paramedian Frontal Flap Reconstruction for Nasal Defect Following an Accidental Amputation
Abstract
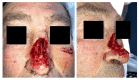
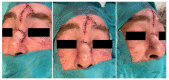
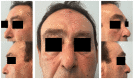
This case report aims to present the successful reconstruction of a nasal defect in a 56-year-old male patient who suffered a partial nasal amputation due to a domestic accident involving a grinding wheel. The reconstruction was carried out using a paramedian frontal flap in a two-stage surgical process. Initially, the flap was designed and customized to match the dimensions of the defect, with a pedicle width of approximately 1.5 cm vertically. The flap was elevated in a distal-to-proximal manner, starting with subcutaneous dissection and progressing to periosteal dissection proximally. Weekly dressing changes were made using fatty gauze and fusidic acid ointment. Four weeks postoperatively, the flap pedicle was divided, and the brow was repositioned. At the six-month follow-up, the patient showed satisfactory clinical outcomes with no functional complaints and was very pleased with the aesthetic result. Paramedian frontal flap reconstruction is a dependable technique for addressing nasal defects following traumatic amputation, providing favorable functional and aesthetic results. This case highlights the importance of careful surgical planning and technique in achieving successful facial reconstruction.
Keywords: facial reconstructive surgery; maxillo-facial trauma; nasal amputation; nasal reconstruction; paramedian frontal flap.
Copyright © 2024, Pereira et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- The paramedian forehead flap: a dynamic anatomical vascular study verifying safety and clinical implications. Reece EM, Schaverien M, Rohrich RJ. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121:1956–1963. - PubMed
-
- Nasal reconstruction by modified bilobed forehead flap. Akbay E, Cokkeser Y, Karaoğlu E. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2012;22:354–357. - PubMed
-
- Paramedian forehead flap for the reconstruction of extensive nasal defects (Article in Spanish) Belmar P, de Eusebio E, Sánchez C, et al. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2011;102:187–192. - PubMed
-
- Refinements in nasal reconstruction: the cross-paramedian forehead flap. Angobaldo J, Marks M. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;123:87–93. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
