Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Moroccan Community Rheumatologists' Regarding the Management of Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: A National Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 38803407
- PMCID: PMC11129670
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.61162
Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Moroccan Community Rheumatologists' Regarding the Management of Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: A National Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
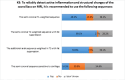
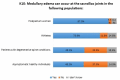
Introduction Non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) is within the spectrum of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). The emergence of the nr-axSpA concept, defined by the absence of significant erosive damage to the sacroiliac joints, has prompted numerous initiatives aimed at enhancing the early detection and management of this condition. The aim of the study was to assess the knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to the diagnosis and management of nr-axSpA by rheumatologists in Morocco. Methods We conducted a cross-sectional online survey among the rheumatologist community in Morocco. Rheumatologists received via e-mail a structured Google Forms (Google Inc., Mountainview, CA) questionnaire divided into four sections: sociodemographic data of rheumatologists, knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to the diagnosis and treatment management of nr-axSpA. Results A total of 110 rheumatologists (mean age of 44±13 years, 77.3% females, median professional experience of 12 years (4, 75; 26.25 years)) participated in the survey (response rate of 25%). Most responders reported a diagnosis delay issue in spondyloarthritis (SpA) (93.6%); 70.9% of rheumatologists incorrectly regarded the 2009 Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) classification criteria for axSpA as diagnostic criteria. Rheumatologists' awareness of recommended magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences for detecting sacroiliac joint inflammation and structural changes in SpA varied significantly, from 69.1% to 14.5%. Their knowledge of additional subchondral edema cases in these joints, beyond SpA, ranged from 48.2% to 87.3%. Almost all rheumatologists believed that the use of sacroiliac MRI would contribute to the early diagnosis of axSpA (97.3%) but could also lead to false positive diagnoses, according to 47.3% of rheumatologists; 73.6% believed that incorrectly using the 2009 ASAS classification criteria as diagnostic criteria in nr-axSpA could also result in false-positive diagnoses. In their practice, 2009 ASAS classification criteria were used as diagnostic criteria in axSpA by 39.1% of rheumatologists. Of the total participants, 91.8% indicated that they approach nr-axSpA similarly to radiographic axial spondyloarthritis, with disparities in recommendations of biological therapies. Conclusion Our survey provides insight into the current status of nr-axSpA management among Moroccan rheumatologists. It also addresses concerns regarding the risk of false positive diagnoses when using the 2009 ASAS classification criteria for axSpA as diagnostic criteria by rheumatologists and the potential risk of misdiagnosis associated with excessive reliance on MRI, despite its utility for early diagnosis.
Keywords: classification criteria; morocco; mri; non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis; rheumatologists.
Copyright © 2024, Kronbi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing rheumatologists' attitudes and utilization of classification criteria for ankylosing spondylitis and axial spondyloarthritis: a global effort.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Mar;40(3):949-954. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05308-9. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32797363
-
[Establishment of the current classification criteria for axial spondylarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and SLE in routine practice of German rheumatologists].Z Rheumatol. 2019 Dec;78(10):979-986. doi: 10.1007/s00393-019-0677-9. Z Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31346705 German.
-
Comparison of Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis and Ankylosing Spondyltis from a Single Rheumatology Hospital in Morocco.Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2020;16(3):240-244. doi: 10.2174/1573397115666190222195923. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2020. PMID: 30806321
-
Understanding the paradigm of non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Feb;40(2):501-512. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05423-7. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32996069 Review.
-
Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA): Advances in Classification, Imaging and Therapy.Rheumatol Ther. 2019 Jun;6(2):165-177. doi: 10.1007/s40744-019-0146-6. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Rheumatol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30788779 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ankylosing spondylitis and axial spondyloarthritis. Taurog JD, Chhabra A, Colbert RA. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2563–2574. - PubMed
-
- Spondyloarthritis in North Africa: an update. Slimani S, Hamdi W, Nassar K, Kalla AA. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40:3401–3410. - PubMed
-
- The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:777–783. - PubMed
-
- Profile of patients with spondyloarthritis in Morocco. Essouiri J, Abourazzak FE, Kona I, Harzy T. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018;14:258–263. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources