Identification of circRNA Expression Profile and Potential Systemic Immune Imbalance Modulation in Premature Rupture of Membranes
- PMID: 38803428
- PMCID: PMC11129912
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/6724914
Identification of circRNA Expression Profile and Potential Systemic Immune Imbalance Modulation in Premature Rupture of Membranes
Abstract
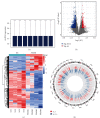
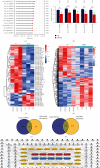
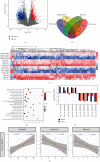
Premature rupture of membrane (PROM) refers to the rupture of membranes before the onset of labor which increases the risk of perinatal morbidity and mortality. Recently, circular RNAs (circRNAs) have emerged as promising regulators of diverse diseases. However, the circRNA expression profiles and potential circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory mechanisms in PROM remain enigmatic. In this study, we displayed the expression profiles of circRNAs and mRNAs in plasma and fetal membranes of PROM and normal control (NC) groups based on circRNA microarray, the Gene Expression Omnibus database, and NCBI's Sequence Read Archive. A total of 1,459 differentially expressed circRNAs (DECs) in PROM were identified, with 406 upregulated and 1,053 downregulated. Then, we constructed the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in PROM, encompassing 22 circRNA-miRNA pairs and 128 miRNA-mRNA pairs. Based on the analysis of gene ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), DECs were implicated in immune-related pathways, with certain alterations persisting even postpartum. Notably, 11 host genes shared by DECs of fetal membrane tissue and prenatal plasma in PROM were significantly implicated in inflammatory processes and extracellular matrix regulation. Our results suggest that structurally stable circRNAs may predispose to PROM by mediating systemic immune imbalances, including peripheral leukocyte disorganization, local immune imbalance at the maternal-fetal interface, and local collagen disruption. This is the first time to decipher a landscape on circRNAs of PROM, reveals the pathogenic cause of PROM from the perspective of circRNA, and opens up a new direction for the diagnosis and treatment of PROM.
Copyright © 2024 Dongni Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lorthe E., Torchin H., Delorme P., et al. Preterm premature rupture of membranes at 22–25 weeks’ gestation: perinatal and 2-year outcomes within a national population-based study (EPIPAGE-2) American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology . 2018;219(3):298.e1–298.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.05.029. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

