A systematic review of the mechanism of action and potential medicinal value of codonopsis pilosula in diseases
- PMID: 38803438
- PMCID: PMC11128667
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1415147
A systematic review of the mechanism of action and potential medicinal value of codonopsis pilosula in diseases
Abstract
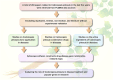
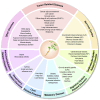
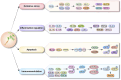
As a traditional Chinese medicinal herb with a long history, Codonopsis pilosula (CP) has attracted much attention from the medical community in recent years. This review summarizes the research progress of CP in the medical field in the past 5 years. By searching and analyzing the literature, and combining with Cytoscape software, we comprehensively examined the role and mechanism of action of CP in individual application, combination drug application, and the role and mechanism of action of codonopsis pilosula's active ingredients in a variety of diseases. It also analyzes the medicinal use of CP and its application value in medicine. This review found that CP mainly manifests important roles in several diseases, such as cardiovascular system, nervous system, digestive system, immune system, etc., and regulates the development of many diseases mainly through the mechanisms of inflammation regulation, oxidative stress, immunomodulation and apoptosis. Its rich pharmacological activities and diverse medicinal effects endow CP with broad prospects and application values. This review provides valuable reference and guidance for the further development of CP in traditional Chinese medicine.
Keywords: active ingredients; codonopsis pilosula (CP); combination drugs; cytoscape; diseases.
Copyright © 2024 Guo, Lou, Hou, Han, Guo, Li, Guan, Liu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Systematic Review of the Phytochemical Profile and Potential Medicinal Functions of Codonopsis pilosula in Cancer.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Feb 24;13(3):e70054. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70054. eCollection 2025 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40008240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effect of different fertilization treatments on yield and secondary metabolites of Codonopsis pilosula].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Aug;42(15):2946-2953. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170714.009. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29139262 Chinese.
-
Research status and future focus on Codonopsis pilosula: A bibliometric analysis of past and present studies.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 5;10(22):e40069. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40069. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39619575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Klebsiella michiganensis LDS17 on Codonopsis pilosula growth, rhizosphere soil enzyme activities, and microflora, and genome-wide analysis of plant growth-promoting genes.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 May 2;12(5):e0405623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04056-23. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38563743 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of network pharmacology and molecular docking technology reveals the mechanism of the herbal pairing of Codonopsis Pilosula (Franch.) Nannf and Astragalus Membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge on chronic heart failure.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jul;10(7):7942-7959. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1469. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34353081
Cited by
-
The mechanistic study of codonopsis pilosula on laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma based on network pharmacology and experimental validation.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 25;16:1542116. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1542116. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40351428 Free PMC article.
-
Fermented Codonopsis pilosula residue improved milk performance of lactating donkeys by enhancing antioxidant capacity and regulating metabolism.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Nov 18;11:1489480. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1489480. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39624060 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects of Huangqi formula (Eefooton) in chronic kidney disease: clinical research and narrative literature review.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Dec 7;16(22):13627-13647. doi: 10.18632/aging.206170. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 39652245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptogens in Long-Lasting Brain Fatigue: An Insight from Systems Biology and Network Pharmacology.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 15;18(2):261. doi: 10.3390/ph18020261. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvement on mitochondrial energy metabolism of Codonopsis pilosula (Franch.) Nannf. polysaccharide.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 30;16:1545356. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1545356. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40520160 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

