The rise of Parkinson's disease is a global challenge, but efforts to tackle this must begin at a national level: a protocol for national digital screening and "eat, move, sleep" lifestyle interventions to prevent or slow the rise of non-communicable diseases in Thailand
- PMID: 38803644
- PMCID: PMC11129688
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1386608
The rise of Parkinson's disease is a global challenge, but efforts to tackle this must begin at a national level: a protocol for national digital screening and "eat, move, sleep" lifestyle interventions to prevent or slow the rise of non-communicable diseases in Thailand
Abstract
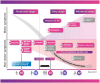
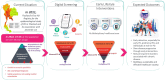
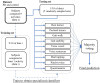
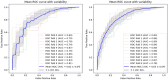
The rising prevalence of Parkinson's disease (PD) globally presents a significant public health challenge for national healthcare systems, particularly in low-to-middle income countries, such as Thailand, which may have insufficient resources to meet these escalating healthcare needs. There are also many undiagnosed cases of early-stage PD, a period when therapeutic interventions would have the most value and least cost. The traditional "passive" approach, whereby clinicians wait for patients with symptomatic PD to seek treatment, is inadequate. Proactive, early identification of PD will allow timely therapeutic interventions, and digital health technologies can be scaled up in the identification and early diagnosis of cases. The Parkinson's disease risk survey (TCTR20231025005) aims to evaluate a digital population screening platform to identify undiagnosed PD cases in the Thai population. Recognizing the long prodromal phase of PD, the target demographic for screening is people aged ≥ 40 years, approximately 20 years before the usual emergence of motor symptoms. Thailand has a highly rated healthcare system with an established universal healthcare program for citizens, making it ideal for deploying a national screening program using digital technology. Designed by a multidisciplinary group of PD experts, the digital platform comprises a 20-item questionnaire about PD symptoms along with objective tests of eight digital markers: voice vowel, voice sentences, resting and postural tremor, alternate finger tapping, a "pinch-to-size" test, gait and balance, with performance recorded using a mobile application and smartphone's sensors. Machine learning tools use the collected data to identify subjects at risk of developing, or with early signs of, PD. This article describes the selection and validation of questionnaire items and digital markers, with results showing the chosen parameters and data analysis methods to be robust, reliable, and reproducible. This digital platform could serve as a model for similar screening strategies for other non-communicable diseases in Thailand.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; Thailand; digital interventions; lifestyle interventions; non-communicable diseases; prevention.
Copyright © 2024 Bhidayasiri, Sringean, Phumphid, Anan, Thanawattano, Deoisres, Panyakaew, Phokaewvarangkul, Maytharakcheep, Buranasrikul, Prasertpan, Khontong, Jagota, Chaisongkram, Jankate, Meesri, Chantadunga, Rattanajun, Sutaphan, Jitpugdee, Chokpatcharavate, Avihingsanon, Sittipunt, Sittitrai, Boonrach, Phonsrithong, Suvanprakorn, Vichitcholchai and Bunnag.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Global health estimates 2020: Disease burden by cause, age, sex by country and by region, 2000–2019. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

