Neuromodulation and the Gut-Brain Axis: Therapeutic Mechanisms and Implications for Gastrointestinal and Neurological Disorders
- PMID: 38804299
- PMCID: PMC11130832
- DOI: 10.3390/pathophysiology31020019
Neuromodulation and the Gut-Brain Axis: Therapeutic Mechanisms and Implications for Gastrointestinal and Neurological Disorders
Abstract
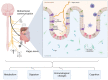
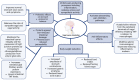
The gut-brain axis (GBA) represents a complex, bidirectional communication network that intricately connects the gastrointestinal tract with the central nervous system (CNS). Understanding and intervening in this axis opens a pathway for therapeutic advancements for neurological and gastrointestinal diseases where the GBA has been proposed to play a role in the pathophysiology. In light of this, the current review assesses the effectiveness of neuromodulation techniques in treating neurological and gastrointestinal disorders by modulating the GBA, involving key elements such as gut microbiota, neurotrophic factors, and proinflammatory cytokines. Through a comprehensive literature review encompassing PubMed, Google Scholar, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library, this research highlights the role played by the GBA in neurological and gastrointestinal diseases, in addition to the impact of neuromodulation on the management of these conditions which include both gastrointestinal (irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)) and neurological disorders (Parkinson's disease (PD), Alzheimer's disease (AD), autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and neuropsychiatric disorders). Despite existing challenges, the ability of neuromodulation to adjust disrupted neural pathways, alleviate pain, and mitigate inflammation is significant in improving the quality of life for patients, thereby offering exciting prospects for future advancements in patient care.
Keywords: deep brain stimulation; gut–brain axis; inflammatory bowel disease; irritable bowel syndrome; neuromodulation; vagus nerve stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enteric nervous system dysfunction as a driver of central nervous system disorders: The Forgotten brain in neurological disease.Neuroscience. 2025 Apr 19;572:232-247. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2025.03.015. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Neuroscience. 2025. PMID: 40088964 Review.
-
Bridging the Mind and Gut: Uncovering the Intricacies of Neurotransmitters, Neuropeptides, and their Influence on Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(1):2-21. doi: 10.2174/0118715249271548231115071021. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38265387 Review.
-
Integrating Gut-Brain Axis: Exploring the Neurogastrointestinal Interactions and Therapeutic Potentials in Autism Spectrum Disorder.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025 Apr 7. doi: 10.2174/0118715303369166250325110016. Online ahead of print. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 40207766
-
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis and Its Therapeutic Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 31;15(21):4631. doi: 10.3390/nu15214631. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37960284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychological comorbidity in gastrointestinal diseases: Update on the brain-gut-microbiome axis.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Apr 20;107:110209. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.110209. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33326819 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut Microbiome Interactions with Oxidative Stress: Mechanisms and Consequences for Health.Pathophysiology. 2024 Jun 21;31(3):309-330. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology31030023. Pathophysiology. 2024. PMID: 39051221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut sensory neurons as regulators of neuro-immune-microbial interactions: from molecular mechanisms to precision therapy for IBD/IBS.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Jul 2;22(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03500-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40605050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status and trends in the study of intestinal flora in cognitive disorders: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 27;16:1577597. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1577597. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40497058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breaking the cycle: Psychological and social dimensions of pediatric functional gastrointestinal disorders.World J Clin Pediatr. 2025 Jun 9;14(2):103323. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i2.103323. eCollection 2025 Jun 9. World J Clin Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40491742 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative Interventions: Postbiotics and Psychobiotics in Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Jun 27. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10632-0. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 40576748 Review.
References
-
- D’Antongiovanni V., Pellegrini C., Antonioli L., Ippolito C., Segnani C., Benvenuti L., D’Amati A., Errede M., Virgintino D., Fornai M., et al. Enteric Glia and Brain Astroglia: Complex Communication in Health and Disease along the Gut-Brain Axis. Neuroscientist. 2023:107385842311634. doi: 10.1177/10738584231163460. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources