A Narrative Review of the State of the Art of CCR4-Based Therapies in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas: Focus on Mogamulizumab and Future Treatments
- PMID: 38804300
- PMCID: PMC11130839
- DOI: 10.3390/antib13020032
A Narrative Review of the State of the Art of CCR4-Based Therapies in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas: Focus on Mogamulizumab and Future Treatments
Abstract
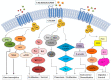
The CCR4 receptor is a pivotal target in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) therapy due to its role in impairing immune responses against malignant T-cells and expression profiles. Monoclonal antibodies like mogamulizumab effectively bind to CCR4, reducing tumour burden and enhancing patient outcomes by inhibiting the receptor's interaction with ligands, thereby hindering malignant T-cell migration and survival. Combining CCR4 antibodies with chemotherapy, radiation, and other drugs is being explored for synergistic effects. Additionally, small-molecular inhibitors, old pharmacological agents interacting with CCR4, and CAR-T therapies are under investigation. Challenges include drug resistance, off-target effects, and patient selection, addressed through ongoing trials refining protocols and identifying biomarkers. Despite advancements, real-life data for most of the emerging treatments are needed to temper expectations. In conclusion, CCR4-targeted therapies show promise for CTCL management, but challenges persist. Continued research aims to optimise treatments, enhance outcomes, and transform CTCL management. This review aims to elucidate the biological rationale and the several agents under various stages of development and clinical evaluation with the actual known data.
Keywords: CCR4; CTCL; chemokine; cutaneous; inflammatory; lymphoma; mediators; oncology; protein; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pileri A., Morsia E., Zengarini C., Torre E., Goteri G., Quaglino P., Pimpinelli N., Paulli M., Pileri S.A., Zinzani P.L., et al. Epidemiology of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas: State of the art and a focus on the Italian Marche region. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2023;33:360–367. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2023.4531. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources