Topologically Protected Photovoltaics in Bi Nanoribbons
- PMID: 38804328
- PMCID: PMC11157647
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c01277
Topologically Protected Photovoltaics in Bi Nanoribbons
Abstract
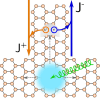
Photovoltaic efficiency in solar cells is hindered by many unwanted effects. Radiative channels (emission of photons) sometimes mediated by nonradiative ones (emission of phonons) are principally responsible for the decrease in exciton population before charge separation can take place. One such mechanism is electron-hole recombination at surfaces or defects where the in-gap edge states serve as the nonradiative channels. In topological insulators (TIs), which are rarely explored from an optoelectronics standpoint, we show that their characteristic surface states constitute a nonradiative decay channel that can be exploited to generate a protected photovoltaic current. Focusing on two-dimensional TIs, and specifically for illustration purposes on a Bi(111) monolayer, we obtain the transition rates from the bulk excitons to the edge states. By breaking the appropriate symmetries of the system, one can induce an edge charge accumulation and edge currents under illumination, demonstrating the potential of TI nanoribbons for photovoltaics.
Keywords: Exciton; Optics; Photovoltaics; Topological insulator; Two-dimensional materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
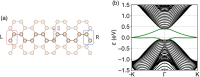
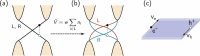
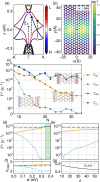
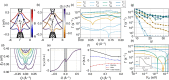
 of the bands. (c) Transition rates of the
ground-state exciton as a function of Q for N = 14. (d) Low-energy exciton band structure. Each color
corresponds to four excitonic states in total. (e) Center-of-mass
velocity of the ground-state exciton. The shadowed region denotes
the fraction of excitons that do not contribute to the formation of
an edge current. (f) Velocity v = ve – vh of the relevant
electron–hole pair
of the bands. (c) Transition rates of the
ground-state exciton as a function of Q for N = 14. (d) Low-energy exciton band structure. Each color
corresponds to four excitonic states in total. (e) Center-of-mass
velocity of the ground-state exciton. The shadowed region denotes
the fraction of excitons that do not contribute to the formation of
an edge current. (f) Velocity v = ve – vh of the relevant
electron–hole pair  and of each component individually, for N = 14 and w = 0.2 eV. (g) Transition rates
as a function of N for Q = 0.1 Å–1 and w = 0.2 eV. (h) Transition rates
as a function of the staggered potential Vst for N = 14 and w = 0.2 eV. The inset shows the total spin projection of the ground-state
exciton,
and of each component individually, for N = 14 and w = 0.2 eV. (g) Transition rates
as a function of N for Q = 0.1 Å–1 and w = 0.2 eV. (h) Transition rates
as a function of the staggered potential Vst for N = 14 and w = 0.2 eV. The inset shows the total spin projection of the ground-state
exciton,  , as a function of the staggered potential.
, as a function of the staggered potential.Similar articles
-
Observation of chiral surface excitons in a topological insulator Bi2Se3.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 5;116(10):4006-4011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1813514116. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30787189 Free PMC article.
-
Realization of a one-dimensional topological insulator in ultrathin germanene nanoribbons.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 28;16(1):2059. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57147-4. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40021624 Free PMC article.
-
Quantum spin Hall insulators and topological Rashba-splitting edge states in two-dimensional CX3 (X = Sb, Bi).Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021 Jan 28;23(3):2134-2140. doi: 10.1039/d0cp05374k. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021. PMID: 33437975
-
Topological properties determined by atomic buckling in self-assembled ultrathin Bi(110).Nano Lett. 2015 Jan 14;15(1):80-7. doi: 10.1021/nl502997v. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Nano Lett. 2015. PMID: 25495154
-
Generation of higher-order topological insulators using periodic driving.J Phys Condens Matter. 2023 Nov 28;36(9). doi: 10.1088/1361-648X/ad0e2d. J Phys Condens Matter. 2023. PMID: 37983922 Review.
References
-
- Rohlfing M.; Louie S. G. Electron-Hole Excitations in Semiconductors and Insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 2312–2315. 10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.2312. - DOI
-
- Onida G.; Reining L.; Rubio A. Electronic excitations: density-functional versus many-body Green’s-function approaches. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 601–659. 10.1103/RevModPhys.74.601. - DOI
-
- Rohlfing M.; Louie S. G. Electron-hole excitations and optical spectra from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 4927–4944. 10.1103/PhysRevB.62.4927. - DOI
-
- Galvani T.; Paleari F.; Miranda H. P. C.; Molina-Sánchez A.; Wirtz L.; Latil S.; Amara H.; Ducastelle F. m. c. Excitons in boron nitride single layer. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 125303.10.1103/PhysRevB.94.125303. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

