Simplifying Data Analysis in Biomedical Research: An Automated, User-Friendly Tool
- PMID: 38804330
- PMCID: PMC11130801
- DOI: 10.3390/mps7030036
Simplifying Data Analysis in Biomedical Research: An Automated, User-Friendly Tool
Abstract
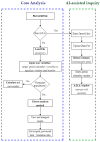
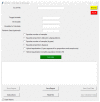
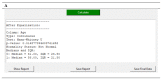
Robust data normalization and analysis are pivotal in biomedical research to ensure that observed differences in populations are directly attributable to the target variable, rather than disparities between control and study groups. ArsHive addresses this challenge using advanced algorithms to normalize populations (e.g., control and study groups) and perform statistical evaluations between demographic, clinical, and other variables within biomedical datasets, resulting in more balanced and unbiased analyses. The tool's functionality extends to comprehensive data reporting, which elucidates the effects of data processing, while maintaining dataset integrity. Additionally, ArsHive is complemented by A.D.A. (Autonomous Digital Assistant), which employs OpenAI's GPT-4 model to assist researchers with inquiries, enhancing the decision-making process. In this proof-of-concept study, we tested ArsHive on three different datasets derived from proprietary data, demonstrating its effectiveness in managing complex clinical and therapeutic information and highlighting its versatility for diverse research fields.
Keywords: LLM models; biomedical research; high dimensional data analysis; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Langley G.R., Adcock I.M., Busquet F., Crofton K.M., Csernok E., Giese C., Heinonen T., Herrmann K., Hofmann-Apitius M., Landesmann B., et al. Towards a 21st-century roadmap for biomedical research and drug discovery: Consensus report and recommendations. Drug Discov. Today. 2017;22:327–339. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2016.10.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frampton G., Whaley P., Bennett M., Bilotta G., Dorne J.-L.C.M., Eales J., James K., Kohl C., Land M., Livoreil B., et al. Principles and framework for assessing the risk of bias for studies included in comparative quantitative environmental systematic reviews. Environ. Evid. 2022;11:12. doi: 10.1186/s13750-022-00264-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

