Humidification during Invasive and Non-Invasive Ventilation: A Starting Tool Kit for Correct Setting
- PMID: 38804382
- PMCID: PMC11130810
- DOI: 10.3390/medsci12020026
Humidification during Invasive and Non-Invasive Ventilation: A Starting Tool Kit for Correct Setting
Abstract
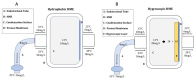
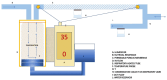
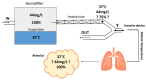
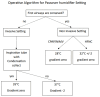
The humidification process of medical gases plays a crucial role in both invasive and non-invasive ventilation, aiming to mitigate the complications arising from bronchial dryness. While passive humidification systems (HME) and active humidification systems are prevalent in routine clinical practice, there is a pressing need for further evaluation of their significance. Additionally, there is often an incomplete understanding of the operational mechanisms of these devices. The current review explores the historical evolution of gas conditioning in clinical practice, from early prototypes to contemporary active and passive humidification systems. It also discusses the physiological principles underlying humidity regulation and provides practical guidance for optimizing humidification parameters in both invasive and non-invasive ventilation modalities. The aim of this review is to elucidate the intricate interplay between temperature, humidity, and patient comfort, emphasizing the importance of individualized approaches to gas conditioning.
Keywords: HME; ICU; active humidification; heated humidifier; pass-over humidifier; passive humidification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gross J.L., Park G.R. Humidification of inspired gases during mechanical ventilation. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012;78:496–502. - PubMed
-
- Doctor T.N., Foster J.P., Stewart A., Tan K., Todd D.A., McGrory L. Heated and humidified inspired gas through heated humidifiers in comparison to non-heated and non-humidified gas in hospitalised neonates receiving respiratory support. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017;2017:CD012549. doi: 10.1002/14651858.cd012549. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

