Core elements of excellent hospital leadership: lessons from the five top-performing hospitals in China
- PMID: 38804900
- PMCID: PMC11168336
- DOI: 10.1093/intqhc/mzae046
Core elements of excellent hospital leadership: lessons from the five top-performing hospitals in China
Abstract
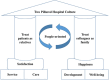
Substantial evidence indicates that leadership plays a critical role in an organization's success. Our study aims to conduct case studies on leadership attributes among China's five top-performing hospitals, examining their common practices. A semi-structured interview was conducted with 8 leaders, 39 managers, 19 doctors, and 16 nurses from the five sample hospitals in China. We collected information from these hospitals on the role of senior leadership, organizational governance, and social responsibility, aligning with the leadership assessment guidelines in the Baldrige Excellence Framework. Qualitative data underwent interpretation through content analysis, thematic analysis, and comparative analysis. This study adhered to the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research guidelines for reporting qualitative research. Our study revealed that the leaders of the five top-performing hospitals in China consistently established "Patient Needs First" as the core element of the hospital culture. Striving to build world-renowned hospitals with Chinese characteristics, the interviewees all believed strongly in scientific vigor, professionalism, and cooperative culture. The leaders adhered to a staff-centered approach, placing special emphasis on talent recruitment and development, creating a compensation system, and fostering a supportive environment conducive to enhancing medical knowledge, skills, and professional ethics. In terms of organizational governance, they continuously enhanced the communication between various departments and levels of staff, improved the quality and safety of medical care, and focused on innovative medical and scientific research, thereby establishing evidence-based, standardized hospital management with a feedback loop. Meanwhile, regarding social responsibility, they prioritized improvements in the quality of healthcare by providing international and domestic medical assistance, community outreach, and other programs. To a large extent, the excellent leadership of China's top-performing hospitals can be attributed to their commitment to a "Two-Pillared Hospital Culture," which prioritizes putting patient needs first and adopting a staff-centered approach. Furthermore, the leaders of these hospitals emphasize hospital performance, operations management, and social responsibility.
Keywords: China; case study; culture; hospital leadership.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of International Society for Quality in Health Care.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
What Makes a Hospital Excellent? A Qualitative Study on the Organization and Management of Five Leading Public Hospitals in China.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2023 Sep 18;16:1915-1927. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S424711. eCollection 2023. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2023. PMID: 37746043 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Care Network in the State of Qatar.Qatar Med J. 2019 Nov 7;2019(2):2. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2019.qccc.2. eCollection 2019. Qatar Med J. 2019. PMID: 31763205 Free PMC article.
-
Studer Group® ' s evidence-based leadership initiatives.J Health Organ Manag. 2015;29(6):684-700. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-10-2013-0211. J Health Organ Manag. 2015. PMID: 26394252
-
Developing leaders at every level: accountability and empowerment actualized through shared governance.J Nurs Adm. 2007 Dec;37(12):564-8. doi: 10.1097/01.NNA.0000302386.76119.22. J Nurs Adm. 2007. PMID: 18090520 Review.
-
Enhancing safety culture in radiology: Key practices and recommendations for sustainable excellence.Radiography (Lond). 2024 Jun;30 Suppl 1:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2024.04.025. Epub 2024 May 25. Radiography (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38797116 Review.
References
-
- Commission NH . China Healthcare Statistics Yearbook (2022). Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press, 2022.
-
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China . Opinions on Strengthening the Performance Evaluation of Tertiary Public Hospitals. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2019-01/30/content_5362266.htm 2019. (30 January 2019, date last accessed).
-
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China . The Opinions on Promoting the High-Quality Development of Public Hospitals. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-06/04/content_5615473.htm 2021. (04 June 2021, date last accessed).